Exploring Yunque National Forest: Conservation Insights

Intro
Yunque National Forest Reservation, nestled in Puerto Rico, is crucial in the discourse of ecological conservation. Its considerable expanse hosts unique flora and fauna, contributing to the island's environmental richness. As the world turns its focus toward biodiversity and the preservation of natural resources, understanding the significance of such natural reserves becomes essential. This article aims to dissect the historical importance of Yunque, the ecosystems it harbors, and the ongoing conservation efforts trying to maintain the delicate balance between human engagement and nature.
Understanding Woodland Ecosystems
Importance of Biodiversity in Forests
Biodiversity is fundamental in maintaining ecological balance. Within Yunque National Forest, various species coexist, each playing a specific role in the environment. These organisms, ranging from towering trees to the diverse animal kingdom, contribute to the resilience of the ecosystem. Healthy forests provide essential services, including clean air, water filtration, and nutrient cycling.
In the context of Puerto Rico, which has faced significant environmental challenges, Yunque stands as a vital refuge for many endangered species. The forest's biodiversity not only supports local economies through eco-tourism but also enhances scientific research opportunities. The intricate relationships among species create a web of life essential for sustainability.
Role of Forests in Climate Regulation
Forests like Yunque act as significant carbon sinks. They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating climate change. As climate patterns shift due to global warming, preserving such forests is critical. Their ability to regulate temperatures and maintain humidity levels significantly impacts regional weather patterns.
"Forests are crucial in carbon mitigation strategies, providing a natural solution that complements technological innovations."
The structural complexity of Yunque's ecosystem, with its layers of vegetation, fosters microenvironments that help stabilize local climates. This stability is key for both the forest's health and surrounding communities.
Sustainable Forestry Practices
Principles of Sustainable Forestry
Sustainable forestry balances ecological, social, and economic objectives. It is centered on responsible forest management that considers long-term impacts rather than short-term gains. In Yunque, sustainable practices focus on maintaining biodiversity while allowing for selective harvesting and recreation. This approach aims to reduce the environmental footprint.
Practices include:
- Protection of waterways
- Minimization of soil erosion
- Use of native species in reforestation efforts
Implementing these guidelines helps maintain the health of Yunque and supports its various ecological functions.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Several initiatives illustrate the success of sustainable forestry in Yunque. One prominent project involves the restoration of native species to combat invasive plant growth. This initiative not only supports local biodiversity but also enhances disaster resilience. Another case includes community engagement programs where local residents are educated on sustainable practices, promoting stewardship of the forest.
Woodland Stewardship Techniques
Forest Management Plans
Effective management of Yunque requires comprehensive planning. These plans integrate scientific research, community needs, and ecological data to create actionable strategies. Regular assessments ensure that the management approaches adapt to changing environmental conditions while still meeting conservation goals.
Conservation Strategies
Key strategies employed for conservation involve habitat restoration, protected area establishment, and species monitoring. Partnerships with academic institutions bolster research and promote awareness. Prioritizing education about the forest's value can enhance community involvement in conservation efforts.
Prelims to Yunque National Forest Reservation
Yunque National Forest is a critical area in Puerto Rico that plays a significant role in the conservation of biodiversity. This reservation features dense, lush forests, unique species, and a complex ecosystem. Its importance can be measured in several ways, both in ecological and cultural terms. As the only tropical rainforest in the United States National Forest System, it houses a variety of flora and fauna which would otherwise be lost. Protecting these natural resources is crucial for sustaining the environment in the region.
Moreover, the reserve acts as a repository of Puerto Rican heritage. The various ecosystems are not just home to numerous plant and animal species; they also provide vital resources to local communities. It is essential to understand the implications of preserving Yunque, from its contributions to global biodiversity to its status as a living classroom for sustainability and ecological studies.
Geographical Context
Yunque National Forest is located in the mountainous region of Puerto Rico, specifically in the Luquillo Mountains. Covering approximately 28,000 acres, the area is characterized by diverse habitats ranging from lowland rainforests to higher montane forests. The terrain varies significantly with elevations reaching up to 3,500 feet, which leads to changes in climate, vegetation, and wildlife. This geographical variation contributes to the rich biodiversity found within the reservation.
The forest is nourished by a combination of high annual rainfall, typically around 200 inches, and a humid, tropical climate. These factors create a microclimate conducive to the growth of many unique species. The elevation gradient influences not only the climate conditions but also the types of vegetation, creating distinct ecosystems within the national forest.
Established in the National Forest System
Yunque was established as part of the National Forest System in 1903, making it one of the oldest national forests in the United States. Its establishment was a direct response to the need for conservation in an era marked by industrialization and rampant deforestation. This proactive approach to conservation illustrates the foresight of policymakers at the time.
Since its designation, the Yunque has undergone various management strategies aimed at preserving its natural resources while accommodating recreational use. Together with the US Forest Service, numerous initiatives have been implemented, focusing on both restoration efforts and sustainable tourism. The dual priority of conservation and recreation helps ensure the forest remains a valuable resource for both present and future generations.
"The establishment of Yunque National Forest as part of the National Forest System reflects a commitment to protecting unique ecosystems and engaging the public in nature conservation."
These efforts have enabled the forest to retain its ecological integrity while also keeping it accessible. Through regulated recreational activities, visitors can experience the beauty and complexity of this unique tropical rainforest while also promoting awareness about conservation practices.
Historical Significance
The historical significance of Yunque National Forest resonates through its role as both a sanctuary and a site of human interaction with nature. This forest is not merely a geographical location; it embodies centuries of ecological stewardship and cultural practices. Understanding its past gives insight into current conservation efforts, as historical successes and failures always inform modern strategy.
Indigenous Influences
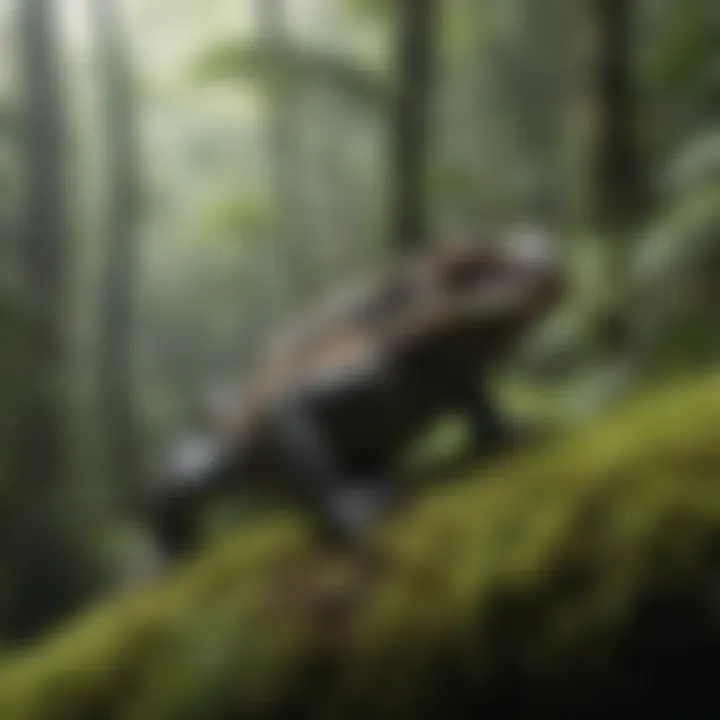


The roots of human interaction with Yunque delve deep into the indigenous Taino people, who inhabited Puerto Rico before European contact. The Taino had a profound understanding of the natural world. They utilized the forest’s resources, not only for sustenance but also for cultural and spiritual practices. Crop cultivation, such as cassava and various fruits, was intricately linked with sacred rituals and serve as a reminder of the need for responsible resource management in and around the forest.
As stewards of the land, the Taino respected the dynamics of the ecosystem and transferred their knowledge across generations. The indigenous influence provides a framework for current conservation practices, emphasizing the importance of sustainability. Restoration initiatives today can draw lessons from Taino agricultural techniques that aimed to harmonize land use with ecological health.
Development through the Years
With the arrival of Europeans, the relationship with Yunque began to change drastically. Colonial exploitation led to significant deforestation, resource extraction, and habitat destruction, profoundly disturbing the ecological balance. The establishment of sugarcane plantations in the 18th century contributed to this rapid degradation. However, as global awareness of environmental issues grew in the 20th century, so did the recognition of Yunque's ecological and cultural value.
In 1903, Yunque was designated as a forest reserve, marking the beginning of a conscious effort to protect this jewel of biodiversity. This decision reflected a larger, emerging understanding of the need to conserve natural spaces. Over the decades, federal protection has been reinforced through various policies aimed at habitat preservation and restoration, bolstered by research and advocacy from multiple environmental agencies.
"Recognizing Yunque's historical context is fundamental to understanding its current conservation goals. It is a story of resilience and adaptation through time."
Yunque National Forest now represents a fusion of its indigenous heritage and modern conservation successes. Its ongoing narrative reflects both the struggles and triumphs in balancing human impact with ecological preservation. This historical backdrop shapes today’s conservation strategies, ensuring that the lessons of the past remain at the forefront of efforts aimed at sustaining this vital reserve.
Ecosystem Diversity
Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of ecosystems within a specific geographical area, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and stability of our planet. At Yunque National Forest Reservation, this diversity is particularly vital due to its unique tropical rainforest environment. The intricate relationships between the flora and fauna support various processes, such as nutrient cycling, climate regulation, and erosion control. In this section, we will delve into the diverse ecosystems that characterize Yunque, emphasizing their significance in conservation efforts and biodiversity.
Flora of Yunque
Endemic Species
Endemic species are plants or animals that are unique to a specific location, making them particularly significant in the context of conservation. In Yunque, a range of endemic flora exists, showcasing the forest's distinct ecological identity. These species have evolved over time, adapting to the local climate and soil conditions. One notable endemic species is the Dacryodes excelsa, commonly known as the Dominican cedar. Its unique characteristic lies in its ability to thrive in the moist, mountainous environments of the forest. This adaptation allows it to contribute to local biodiversity, making it a beneficial component for ecosystem balance by providing shelter and food for various organisms.
However, the limited geographical distribution of these endemic species also poses risks. They can be more vulnerable to environmental changes and human activities, which can disrupt their fragile ecosystems.
Medicinal Plants
Medicinal plants in Yunque play an essential role in traditional and modern medicine. Various species have been identified for their health benefits, including the use of plants like Plantago major for its anti-inflammatory properties. This characteristic fosters local knowledge regarding natural remedies, further linking human health with ecological preservation. The conservation of these plants is beneficial, as it promotes sustainable use and research opportunities in pharmacology.
A unique feature of medicinal plants in Yunque is their adaptability to the rainforest's microclimates. This adaptability allows for a diverse range of compounds to be produced, aiding in numerous health applications. The challenge lies in ensuring that these resources are sustainably harvested and protected from habitat destruction.
Fauna of Yunque
Bird Species
Yunque is home to a fascinating diversity of bird species, many of which are endemic. The Puerto Rican Tody (Todus griseus) is one such bird characterized by its vibrant colors and unique vocalizations. Its role in the ecosystem is vital as it contributes to insect control and seed dispersal. The significant presence of these endemic birds enhances Yunque's attractiveness as a site for birdwatching and ecological studies, making it popular among researchers and ecotourists alike.
However, the habitat preferences of these birds can make them susceptible to changes in their environment. Human encroachment and climate change threaten their habitats, and conservation efforts are essential to maintain their populations.
Terrestrial Wildlife
The terrestrial wildlife of Yunque encompasses a variety of species, including mammals, reptiles, and amphibians that inhabit its lush forests. The Puerto Rican parrot (Amazona vittata) is notable for its endangered status and efforts made for its recovery. This parrot's presence symbolizes the fragility of ecological balance within the forest. Its characteristic is its striking green plumage, which helps it blend into the foliage of the rainforest, making it a unique visual focal point and pivotal for biodiversity.
Maintaining these wildlife populations is vital for the ecosystem’s health. The unique feature of terrestrial wildlife in Yunque lies in their interdependence on specific habitats and food sources. Conservation initiatives must address the aspects of habitat preservation to ensure these species can thrive.
"The biodiversity of Yunque National Forest serves not just as a reservoir of biological richness but as a laboratory for ecological resilience and adaptation."
Through continued research, awareness, and community involvement, Yunque National Forest can serve as a model for conservation, demonstrating the intrinsic value of protecting ecosystem diversity.
Environmental Challenges
The resilience of Yunque National Forest faces numerous environmental challenges that threaten its ecological integrity. Understanding these challenges is pivotal for developing effective conservation strategies. This section explores two primary concerns: the impact of climate change and the management of invasive species.
Climate Change Impact
Climate change is a pressing global issue that has far-reaching effects on ecosystems, and Yunque is no exception. The forest's unique climate conditions create a delicate balance that is increasingly disrupted by rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns.
The impacts of climate change on Yunque can be summarized in several key areas:
- Temperature Increases: Higher temperatures can alter the composition of plant and animal species, pushing them beyond their adaptive limits.
- Shifts in Rainfall: Changes in rainfall patterns can lead to droughts in some areas while increasing susceptibility to flooding in others.
- Disruption of Ecosystems: Each of these factors contributes to habitat loss and degradation, threatening endemic species that rely on specific climate conditions.
"Yunque National Forest represents a biodiversity hotspot, but climate change poses a significant threat that may lead to irreversible losses."
Monitoring these changes is crucial, allowing conservationists to implement adaptive management practices. Strategies may include relocating species at risk, adjusting forest management plans, and increasing ecosystem connectivity.
Invasive Species Management
Invasive species are another considerable challenge for Yunque National Forest. These non-native organisms can outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to native species, ultimately leading to degradation of the forest's biodiversity.
Effective management of invasive species requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Identification: Recognizing invasive species is the first step. Some common examples in Yunque include the African tulip tree and the feral pig.
- Control Measures: Techniques to control invasive populations can involve mechanical removal, chemical treatments, and promoting the growth of native species.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in monitoring and control can strengthen efforts. Educational programs can raise awareness about the importance of maintaining native biodiversity.


The management of invasive species not only protects the unique flora and fauna of Yunque but also supports the larger goal of preserving the forest as a vital ecosystem amidst a changing environment.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts in Yunque National Forest are crucial for maintaining the ecological integrity of this unique landscape. They facilitate the protection of various species and their habitats, and they foster a balanced relationship between nature and human activity. Through multiple initiatives, stakeholders aim to ensure that the rich biodiversity present in this forest is preserved for future generations. Effective conservation strategies not only contribute to environmental health but also bolster Puerto Rico's economy through sustainable tourism and research.
Research Initiatives
Research initiatives play a central role in the conservation strategy for Yunque. They help gather essential data on the various species, ecosystems, and processes occurring within the reserve. Academic partnerships with universities and research institutions lead to several projects focused on areas such as species monitoring, habitat restoration, and climate impact assessments.
Some significant projects include:
- Biodiversity Surveys: Regular evaluations identify the rich variety of plants and animals living in Yunque, many of which are endemic.
- Climate Change Studies: Researchers observe how shifting weather patterns affect species and ecosystems, providing guidance for adaptation strategies.
The data derived from these efforts not only informs conservation policies but also educates local communities about the ecological significance of their natural surroundings. By underlining the importance of science in conservation, these initiatives engage a broader audience in protective measures.
Community-Based Conservation
Community-based conservation emphasizes the role of local populations in safeguarding their environment. In Yunque, this approach recognizes that local knowledge and cultural practices are invaluable in conservation efforts. Community engagement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility toward natural resources.
In Yunque, community initiatives might include:
- Sustainability Workshops: Educating residents on sustainable practices that benefit both the environment and local livelihoods.
- Volunteering Programs: Involving local individuals in restoration projects, enhancing their connection to the forest.
- Cultural Exchange: Highlighting indigenous methods of conservation, promoting traditional knowledge as part of ecological stewardship.
This blend of modern conservation science with traditional practice creates resilience against external threats such as climate change and invasive species.
Community involvement is soft, yet powerful—local commitments can lead to significant environmental change.
Overall, the combination of research initiatives and community-based conservation efforts forms a robust strategy that assures the continued vitality and biodiversity of Yunque National Forest.
Visitor Engagement and Education
Visitor engagement and education are critical components for the sustainable management of Yunque National Forest. By providing visitors with knowledge and understanding about the forest's significance, conservation practices can be reinforced. An informed public is more likely to value and protect natural resources. This section elaborates on how visitor engagement and education facilitate positive experiences while emphasizing the forest's ecological value.
Guided Tours and Workshops
Guided tours and workshops play an essential role in visitor engagement at Yunque National Forest. These programs offer structured opportunities for participants to learn about the unique ecosystems, rich biodiversity, and conservation efforts within the forest. Knowledgeable guides usually lead these tours, which help to enhance the visitor experience. They share insights on various species, habitats, and the significance of preservation efforts.
Some benefits of guided tours include:
- Expert Insights: Professional guides provide valuable information that might be overlooked in self-guided tours.
- Interactive Learning: Participants can ask questions, interact with the environment, and learn in a hands-on manner.
- Community Building: Group tours help foster a sense of connection among participants, leading to discussions about conservation and ecological awareness.
Workshops provide another layer of education by delving into more specific topics such as plant identification, birdwatching, and sustainable practices. Attendees leave with increased understanding and skills that promote stewardship.
Visitor Center Resources
The Visitor Center is a cornerstone of engagement and education in Yunque National Forest. It serves as an informational hub for guests to learn more about the forest's ecological and cultural significance. The resources available at the center include maps, brochures, and educational exhibits that highlight conservation efforts, historical context, and details of native species.
Additional offerings at the Visitor Center include:
- Interactive Displays: Engaging exhibits allow visitors to discover more about species and ecosystems in Yunque.
- Educational Programs: Regularly scheduled programs are tailored for different age groups, ensuring that educational content is accessible to all.
- Volunteer Programs: Opportunities to participate in conservation efforts encourage visitors to take an active role in preserving the forest.
By utilizing these resources, visitors gain a deeper appreciation for Yunque's natural treasures, which can inspire ongoing commitment to conservation.
"Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world."
— Nelson Mandela
Through focused education and engagement, Yunque National Forest can ensure that its unique biodiversity and ecosystems are valued and protected for generations to come.
The Role of Yunque in Global Conservation
Yunque National Forest is not just a local gem; it plays an invaluable role in global conservation efforts. This forest is home to a rich tapestry of biodiversity that underpins numerous ecological processes. Understanding its contributions helps contextualize the broader implications for environmental preservation worldwide.
Yunque’s unique ecosystems are crucial for maintaining various natural balances. This area acts as a reservoir for many endemic species, serving as a refuge for organisms that might otherwise be lost to habitat destruction and climate change. Such areas are essential not only for local biodiversity but also for enhancing global ecological resilience. In an era where significant environmental challenges lurk on the horizon, Yunque provides a compelling case for integrated conservation strategies.
"The health of Yunque directly correlates with the global health of ecosystems."
Biodiversity Hotspot
Emphasizing its status as a biodiversity hotspot, Yunque boasts a multitude of life forms. Flora and fauna endemic to this region contribute to its uniqueness. Among the forest's splendor are species like the Puerto Rican Parrot and Tabebuia heterophylla, both of which emphasize the forest’s rich and distinct ecological narrative. These species provide critical ecological services that deter the spread of invasive species and support food webs within the local ecosystem.
Key Benefits of its Biodiversity:
- Ecological Stability: A diverse ecosystem promotes stability, essential for resilience against climate variances.
- Genetic Resources: Endemic species can provide genetic materials vital for research and agricultural advancements.
- Cultural Importance: The biodiversity of Yunque is interwoven with cultural traditions and practices, enhancing local identity and heritage.

Collaboration with International Bodies
Yunque National Forest serves as a focal point for international conservation efforts. Collaboration occurs through partnerships with organizations like the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and various non-governmental organizations. These partnerships aim to develop frameworks that foster sustainable practices, monitor ecological impacts, and implement protective measures.
Such collaborations enhance knowledge sharing and resource allocation, fostering a global understanding of best practices in conservation. These relationships boost research capabilities, allowing scientists to study Yunque's biodiversity at a broader scale. They also enable the dissemination of findings to policymakers and conservation practitioners worldwide.
Collaborative Initiatives:
- Research Projects: Joint studies focusing on the effects of climate change on endemic species.
- Educational Programs: Training workshops for local communities on sustainable practices involving collaboration across nations.
- Conservation Campaigns: Global awareness campaigns leveraging Yunque's biodiversity as a model for conservation efforts.
Cultural Significance of Yunque
The cultural significance of Yunque National Forest is profound and multifaceted. It holds a unique place in Puerto Rico's history, intimately tied to the heritage and traditions of the indigenous Taíno people and later Spanish colonial influences. The forest is not just a collection of trees; it represents a living archive of the island’s culture and ecosystems. This connection to the land is vital for understanding the interplay between natural and cultural heritage. The preservation of Yunque is essential for maintaining cultural practices and traditions that have persisted through generations.
In Yunque, cultural practices derive from the natural environment. The diverse flora and fauna have played a critical role in the traditions of local communities. Many plants found in Yunque are vital for traditional cooking, medicine, and rituals. The systematic study of these practices reveals not only the connections between biodiversity and local cultures but also highlights the importance of continuing these traditions in modern society.
Cultural Practices and Traditions
Cultural traditions associated with Yunque are deeply rooted in the landscape. Local communities engage in various practices that celebrate the ecological richness of the forest. For instance, many families participate in harvesting medicinal plants, which is a practice passed down through generations. Such customs not only foster a connection to the environment but also maintain traditional knowledge systems that have significant value in contemporary society.
Various festivals and community events revolve around themes of nature and conservation. These gatherings serve as platforms for education and awareness about the forest's biodiversity. Activities often include guided hikes, workshops about native cooking with local ingredients, and storytelling sessions that recount the history and significance of the forest. These events reinforce the community’s bond with Yunque and educate visitors about the cultural significance of the area.
The interdependence of cultural practices and environmental stewardship in Yunque offers a unique model for sustainable living, blending tradition with conservation.
Spiritual Connection to Nature
The spiritual connection of the communities to Yunque National Forest reflects a profound respect for nature. Many locals perceive the forest as a sacred space that embodies a connection to their ancestors and the spirits of the land. This belief is central to understanding the ethos of conservation present in local practices. For many individuals, visiting the forest is not only a recreational act but a spiritual pilgrimage that reconnects them with their roots and the natural world.
Traditional beliefs hold that the spirits of the ancestors are intertwined with the forest, offering guidance and protection. Rituals and offerings may be made in specific locations within Yunque as a means of honoring these traditions. Such spirituality fosters an environmental consciousness that promotes the preservation of biodiversity and respect for ecosystems.
As climate change threatens these natural areas, the spiritual connection grows even more critical. Protecting Yunque is seen not just as a matter of environmental conservation but as an act of reverence for cultural identity and heritage.
"Nature does not hurry, yet everything is accomplished."
This quote encapsulates the philosophy that underpins the relationship of the communities with Yunque, signifying a balanced approach to life that integrates respect for the natural world.
Through understanding the cultural significance of Yunque, we also address broader themes of conservation, identity, and community resilience. This holistic view is essential for effective stewardship in the face of ecological challenges.
Sustainable Forestry Practices
Sustainable forestry practices are essential to preserving the ecological integrity of Yunque National Forest. These practices aim to manage forest resources in a way that satisfies current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This involves maintaining biodiversity, enhancing productivity, and ensuring the ecological health of the forest.
A key aspect of sustainable forestry is implementing comprehensive forest management techniques. These techniques can include selective logging, reforestation, and controlled burns. Selective logging helps to maintain the forest's biodiversity by allowing certain trees to thrive while still obtaining timber. Reforestation involves planting native trees to replenish areas where trees have been harvested or that have suffered damage. Controlled burns, on the other hand, can reduce the buildup of combustible material, thus preventing larger, uncontrollable wildfires. The importance of these methods cannot be overstated, as they contribute significantly to both the resilience of the forest and the mitigation of climate change impacts.
Forest Management Techniques
Forest management techniques in Yunque National Forest are critical to ensuring the forest can sustain itself while providing for local community needs.
- Selective Logging: This method reduces the ecological footprint of timber harvests. By allowing some trees to remain, the practice supports wildlife habitats and preserves the underlying ecosystem.
- Reforestation: The introduction of native species is encouraged to maintain genetic diversity. Planting species such as the Tabebuia heterophylla or the Guaiacum sanctum aids in the recovery of ecosystems and contributes to overall forest health.
- Controlled Burn: This method is used to manage underbrush, which can help to foster the growth of native species and prevent pests. With careful timing and conditions, it can support a healthy ecosystem while minimizing risks of larger fires.
These techniques not only promote a healthier forest environment but also sustain the livelihoods of communities relying on forestry.
Impact of Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices have a far-reaching impact on the ecological, social, and economic aspects of Yunque National Forest. They support a balanced ecosystem that can adapt to changing environmental conditions, thus enhancing the forest's resilience against climate change.
Benefits of sustainable practices include:
- Biodiversity Conservation: By preserving various species, sustainable forestry helps protect the genetic diversity necessary for resilience against diseases and pests.
- Soil and Water Conservation: Healthy forests contribute to soil stability and water quality, reducing erosion and maintaining vital water resources.
- Community Benefits: Local economies can thrive through jobs in sustainable logging, eco-tourism, and conservation-related activities.
- Climate Mitigation: Sustainable forests capture carbon, thus helping to mitigate the effects of climate change, an increasingly critical factor in global conservation efforts.
"The balance achieved through sustainable practices ensures that we protect our forests for future generations, combining ecological health with community needs."
As Yunque National Forest navigates forward in the 21st century, sustainable forestry practices will continue to play a crucial role in conserving its rich biodiversity and ensuring its ecological health for years to come.
The Future of Yunque National Forest
The sustainable management and future of Yunque National Forest are among the most critical topics in the broader conversation about ecological preservation. As Puerto Rico's only tropical rainforest, Yunque holds a unique position within the Caribbean's biodiversity landscape. This forest is not simply a treasure of nature but serves as a living laboratory that offers insights into species preservation, climate change adaptation, and ecological resilience. Evaluating its future involves a multi-faceted approach to adaptive management and long-term conservation goals.
Adaptive Management Strategies
Adaptive management strategies for Yunque emphasize the need for a flexible, iterative process to forest management. The objective here is to allow scientists, conservationists, and policymakers to learn from the outcomes of their decisions and adjust their approaches, ensuring the protection of the diverse ecosystems. Some key adaptive management strategies include:
- Monitoring Ecological Changes: Regular assessments of flora and fauna will help track the health of ecosystems. Monitoring can involve studying shifts in species populations and habitat conditions due to climate change and human activities.
- Habitat Restoration Initiatives: When certain areas of the forest experience degradation, targeted restoration efforts can revitalize those habitats. Strategies include reforestation and removal of invasive species that threaten native plants.
- Collaborative Research Projects: Partnering with local and international researchers can provide additional insights and innovative solutions. Collaborative projects can focus on specific issues like water management or pollinator health.
"Adaptive management allows us to respond to changes effectively, ensuring the longevity of resources we depend on."
Long-Term Conservation Goals
Long-term conservation goals for Yunque National Forest must align with both ecological and socio-economic realities. Achieving these goals requires a sustained commitment from various stakeholders, including government agencies, local communities, and environmental organizations. Some prominent goals include:
- Biodiversity Preservation: The protection of endangered and endemic species is essential. This may entail creating biodiversity corridors to ensure safe migration and genetic diversity among species.
- Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about the importance of conservation can galvanize local and international support. Educational programs should target schools and local communities to foster a sense of stewardship.
- Policy Development and Implementation: Effective natural resource policies that mitigate human impact on the forest are vital. Advocating for regulations that support sustainable tourism, land use, and conservation finance will contribute to future successes.
The future of Yunque National Forest hinges on both adaptive management strategies and long-term conservation goals, where each element supports the other. Intentionally fostering a collaborative effort among various stakeholders can lead to effective solutions that honor the forest’s historical and ecological significance.







