A Comprehensive Overview of Skunk Cabbage and its Ecological Significance
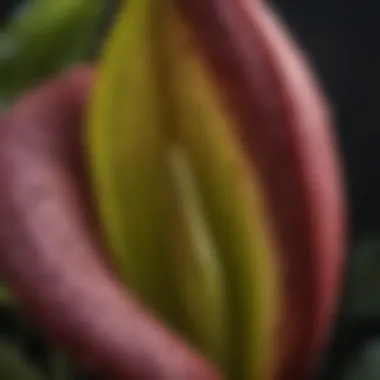
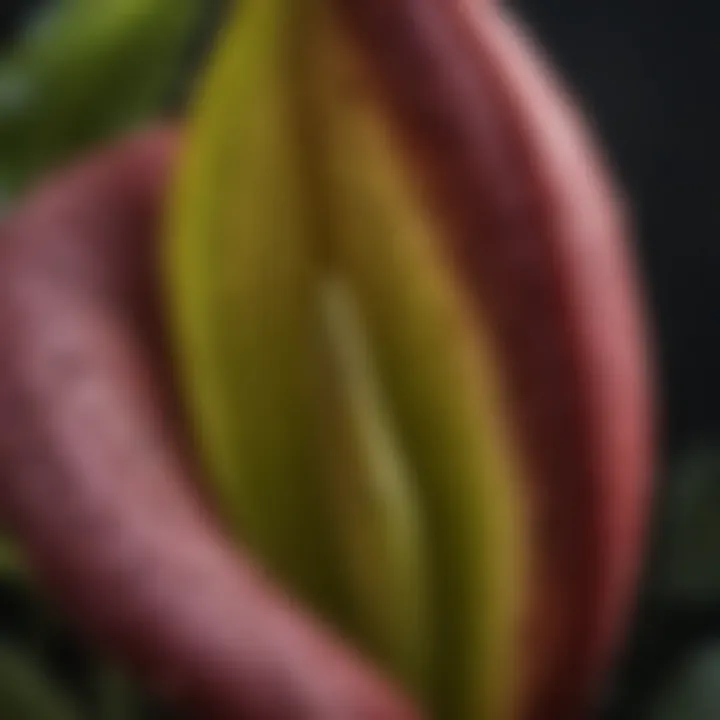
Intro
Skunk cabbage (Symplocarpus foetidus) is a distinctive plant that thrives in wetland environments. Its unique morphology and ecological functions make it an interesting subject for exploration. This section will lay the groundwork for understanding skunk cabbage within the larger context of woodland ecosystems, emphasizing the importance of biodiversity and the role forests play in climate regulation.
Understanding Woodland Ecosystems
Woodland ecosystems are complex networks that sustain a variety of flora and fauna. The presence of diverse species contributes to the resilience of these environments. Biodiversity is not just about the number of species but also their interactions. For instance, skunk cabbage plays a significant role in wetland ecosystems by providing habitat and food for many species, including insects and amphibians.
Importance of Biodiversity in Forests
Biodiversity is crucial for maintaining ecosystem health:
- Varied Species Interactions: Different species perform unique roles which enhance ecosystem functions.
- Resilience to Stress: A diverse ecosystem can better withstand environmental changes and disasters.
- Nutrient Cycling: Various organisms contribute to the breakdown of organic matter, enriching soil quality.
Impact on skunk cabbage can be significant; the plant often serves as an early spring food source for various creatures, thus supporting early life cycles in woodland environments.
Role of Forests in Climate Regulation
Forests act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This process mitigates climate change impacts. Furthermore, they help regulate water cycles by facilitating groundwater recharge and maintaining humidity levels. Skunk cabbage, by thriving in wetland areas of these forests, contributes to the overall health of the ecosystem. Its large leaves trap snow and slow down runoff, thus playing a role in maintaining moisture levels in the soil.
"The intricate relationships within forest ecosystems highlight the importance of each species, no matter how seemingly insignificant."
The ecological significance of skunk cabbage extends beyond its physical form; it impacts the entire habitat it occupies. Understanding its role within these broader frameworks is essential for nature enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Sustainable Forestry Practices
To ensure the continued health of woodland ecosystems, sustainable forestry practices must be adopted. This section will explore key principles and case studies that underline successful strategies.
Principles of Sustainable Forestry
Sustainable forestry is based on several core principles:
- Ecosystem Health: Prioritize the maintenance of healthy forest ecosystems.
- Long-Term Viability: Focus on practices that support the forest's long-term ecological and economic health.
- Community Involvement: Engage local communities in forest management decisions.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Examining specific instances of sustainable practices provides narrative richness:
- The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC): Certification program promoting responsible forest management.
- Community Forestry Projects in the Amazon: Local populations manage resources sustainably, safeguarding biodiversity.
These practices demonstrate how integrating ecological principles can lead to better outcomes for both ecosystems and human communities.
Woodland Stewardship Techniques
Effective woodland stewardship techniques are vital for the conservation of natural resources. This section examines management plans and strategies that foster ecological health.
Forest Management Plans
Forest management plans outline how forests are maintained for various purposes:
- Resource Allocation: Determining how much timber or wildlife can be sustainably utilized.
- Protection Measures: Implementing actions to safeguard endangered species or habitats.
Conservation Strategies
Adopting specific conservation strategies ensures the preservation of biodiversity:
- Habitat Restoration: Rehabilitating damaged ecosystems.
- Invasive Species Management: Controlling non-native species that threaten ecological balance.
Through understanding these various aspects, it becomes clear how skunk cabbage fits into the larger picture of woodland stewardship. Its value extends beyond individual species, emphasizing the need for integrated approaches to conservation.
In summary, skunk cabbage, alongside the practices and strategies that promote healthy environments, holds essential value for both ecosystems and human society.
Prologue to Skunk Cabbage
Skunk cabbage, a unique plant found in wetland ecosystems, holds considerable ecological significance. Its distinctive morphology and behavior in the environment have drawn the attention of researchers and nature enthusiasts alike. Understanding skunk cabbage is crucial, as it provides insights into wetland ecology and the various roles that flora can play within these vital ecosystems.
Definition of Skunk Cabbage
Skunk cabbage is the common name for the species Symplocarpus foetidus, a perennial herbaceous plant characterized by its large leaves and unique flowering structure. Native to North America, this plant typically thrives in swampy or marsh-like areas. The name "skunk cabbage" derives from the unpleasant odor emitted by the flower during its blooming phase, which resembles that of skunk spray.
This plant grows early in spring, sometimes even pushing through the snow, making it one of the first flowering plants in its habitat. The hooded flowers are a distinct feature, setting the skunk cabbage apart from other vegetation in the region. It plays a role in the broader ecosystem by providing early spring food sources for wildlife and aiding in soil stabilization.
Historical Context
Historically, skunk cabbage has been a part of indigenous people’s traditions, often used for medicinal purposes. Its roots were utilized for their diuretic properties and to treat a variety of ailments. The plant’s resilience in low-quality soils and its role in nutrient cycling have made it a topic of interest among ecologists as well.
As human activity has increased in wetland areas, awareness regarding the importance of skunk cabbage in these ecosystems has also grown. Conservation efforts today take into account the historical context of the plant, focusing on its preservation and the ecological message it carries about wetland health and biodiversity .
In summary, skunk cabbage is not just an interesting plant but is deeply interwoven with ecological dynamics and human history. Its study helps emphasize the importance of conserving wetland habitats, making it a topic of relevance in both academic circles and conservation discussions.
Taxonomy and Classification


Taxonomy and classification play a crucial role in understanding skunk cabbage and its ecological significance. By categorizing this unique plant, researchers can better comprehend its relationships with other species and its role within wetland ecosystems. Taxonomy provides a structure to study biodiversity, allowing for a systematic approach to conserving species and their habitats. For skunk cabbage specifically, its classification reveals important insights into its ecological niche, adapting mechanisms, and interactions with flora and fauna.
Scientific Classification
Skunk cabbage belongs to the family Araceae, which is also known as the aroid family. This family showcases diverse plants often found in moist environments. The scientific classification of skunk cabbage is as follows:
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Division: Angiosperms
- Class: Monocots
- Order: Alismatales
- Family: Araceae
- Genus: Symplocarpus
- Species: Symplocarpus foetidus
This classification highlights the plant's unique biological characteristics. The genus name "Symplocarpus" refers to the fusion of fruits, illustrating the species' distinctive reproductive structure. The species name "foetidus" indicates its strong odor, which is likened to that of rotting flesh, a key feature for attracting its pollinators.
Genus and Species Overview
The genus Symplocarpus includes a few species, but Symplocarpus foetidus is the most well-known. This plant is often found in swampy areas across North America. Its adaptations to wetland environments showcase its resilience.
Characteristics of Symplocarpus foetidus:
- It produces large, heart-shaped leaves that can grow up to three feet long.
- The flower emerges in a spath, a unique protective structure for the flower cluster.
- Skunk cabbage is known for being one of the first wildflowers to bloom in spring, often poking through the snow.
- Its ability to generate heat helps in melting snow around it, which further supports its early growth cycle.
Understanding the taxonomy of skunk cabbage contributes significantly to its conservation efforts. Knowing its classification helps in identifying suitable habitats and monitoring populations, ensuring the survival of this important wetland species.
"The traditional classification of a plant not only helps in identifying it scientifically but also paves the path for effective conservation strategies."
Morphological Characteristics
Understanding the morphological characteristics of skunk cabbage is essential for recognizing its role in wetlands and its interactions with the ecosystem. Morphology offers insights not just into the plant's appearance but also into its adaptations and survival strategies within its native habitats. Skunk cabbage showcases various traits that contribute to its ecological significance, making it a fascinating subject for exploration.
Leaves and Flowers
Skunk cabbage has large, distinctive leaves that can reach up to 3 feet long. These leaves emerge directly from the ground in early spring, often before the snow has melted. Their broad shape allows for maximum sunlight capture, facilitating effective photosynthesis, which is crucial for growth during the shorter daylight hours of early spring.
The flowering structure of skunk cabbage is equally intriguing. It produces a unique inflorescence called a spadix, surrounded by a hood-like leaf known as a spathe. The spadix can reach heights of up to 12 inches and is notable for its thermogenic ability, meaning it can generate heat. This warmth allows the plant to melt the surrounding snow and attract early pollinators, such as flies and beetles. The color of the spathe typically varies from green to yellow, contributing to the plant's visibility in its native wetland environments.
Roots and Rhizomes
The root system of skunk cabbage consists of fleshy roots and a network of rhizomes. The fleshy roots help in anchoring the plant securely within the saturated soils of its habitat, preventing erosion and facilitating nutrient uptake. The rhizomes serve as critical storage organs, enabling the plant to survive adverse conditions such as fluctuating water levels.
Rhizomes also provide a mechanism for vegetative reproduction. Skunk cabbage can spread through these subterranean stems, establishing new plants close to the parent. This growth strategy is crucial for maintaining populations in wetland areas where competition for space and resources can be intense. The resilience of skunk cabbage, in part due to its morphological traits, allows it to thrive even in challenging conditions, establishing itself as a keystone species in many wetland ecosystems.
The exceptional morphological features of skunk cabbage make it an integral component of wetland health and stability.
In summary, the morphological characteristics of skunk cabbage play a vital role in its ecological function. By examining the interplay between its leaves, flowers, roots, and rhizomes, we gain valuable insights into how skunk cabbage not only survives but thrives in its habitat. This knowledge is essential for forestry professionals and academics focusing on wetland conservation and plant ecology.
Habitat and Distribution
Understanding the habitat and distribution of skunk cabbage is essential to grasp its ecological significance. Skunk cabbage is primarily found in wetland ecosystems, which are critical for maintaining biodiversity and providing various ecosystem services.
Wetland Ecosystems
Skunk cabbage is notably adapted to wetland habitats, thriving in muddy, waterlogged soils. These ecosystems are home to a variety of flora and fauna, each playing a role in the overall health of the environment. Wetlands serve as natural water filters, improving water quality by trapping pollutants and sediments. Furthermore, they act as flood buffers, absorbing excess rainwater and reducing the risk of downstream flooding. The presence of skunk cabbage in these areas is important because it stabilizes soil, reducing erosion, and provides shelter and food for various species.
Skunk cabbage produces a distinct odor that attracts pollinators, such as flies, which are often drawn to its flower structure. This unique interaction contributes to the pollination process, critical for the reproductive success of many plant species within wetland environments.
Geographical Range
Skunk cabbage is primarily distributed across North America, from the eastern United States to parts of Canada. Its range extends from the coastal forests to inland wetlands, highlighting its adaptability to different wetland types. The species prefers rich, moist soils often found in wooded swamps and along streams or riverbanks.
In the United States, skunk cabbage is especially prevalent in states such as New York, Pennsylvania, and Michigan. Its presence indicates a healthy wetland ecosystem, as the plant thrives only under specific environmental conditions, including adequate moisture and suitable nutrient availability. Monitoring its geographical distribution can provide insights into the ecological health of these habitats.
"Distribution of skunk cabbage closely ties to the quality of wetland ecosystems. Its decline can signal impending ecological issues."
As climate change progresses, shifts in the geographical range of skunk cabbage may occur. Alterations in precipitation patterns and temperature could affect its growth and habitat. Professionals in forestry and conservation should be aware of these potential changes and their implications for wetland conservation efforts.
In summary, the habitat and distribution of skunk cabbage are integral to understanding its ecological roles. Recognizing the relationship between this unique plant and its wetland ecosystem can inform conservation strategies to protect these vital habitats.
Ecological Role of Skunk Cabbage
The ecological role of skunk cabbage extends beyond its unique morphology and habitat preferences. This plant plays a vital part in sustaining local ecosystems, affecting both flora and fauna in various ways. Understanding these roles helps appreciate the significance of skunk cabbage in wetland environments.
Food Source for Wildlife
Skunk cabbage serves as a crucial food source for numerous wildlife species. Its early spring emergence provides essential nutrients at a time when many other food sources are scarce. Herbivorous animals, including deer and rabbits, are known to consume the young leaves and flowers. Additionally, various caterpillars and pollinators, such as bees, benefit from its blooms. The plant's high nutrient content aids in the development and survival of these creatures, creating a symbiotic relationship that fosters biodiversity.
It is important to note that skunk cabbage can also influence local food webs. By offering sustenance, it indirectly supports higher trophic levels, impacting the entire ecosystem.
Furthermore, the distinctive smell of skunk cabbage may deter certain herbivores while attracting specific insects that aid in pollination. This complex interaction showcases the plant's role not just as food, but also as part of a dynamic ecological network.
Soil Erosion Control
Another significant ecological role of skunk cabbage lies in its ability to mitigate soil erosion. The plant's extensive rhizome system helps stabilize soil in wetland environments where movement of water can easily displace sediment. By anchoring the soil, skunk cabbage plays a critical role in maintaining the integrity of its habitat, especially during heavy rainfall or flooding events.
The thick leaves of the skunk cabbage also provide cover for the ground, thus reducing surface runoff and allowing for better water absorption. This aspect is particularly crucial in areas where soil quality may be compromised by agriculture or urban development. As a result, preserving skunk cabbage in wetlands not only protects the plant species but also contributes to healthier and more resilient ecosystems.
Cultural Significance


The cultural significance of skunk cabbage extends beyond its ecological roles. It encompasses its uses in traditional medicine and its symbolism in various cultures. Understanding these aspects helps to appreciate the plant's place not just in ecology but also in human interactions with nature.
Uses in Traditional Medicine
Skunk cabbage has a long history in traditional medicine. Various indigenous peoples have utilized the plant for its medicinal properties. The plant contains compounds that have been studied for their potential health benefits. For instance, skunk cabbage has been traditionally used to treat respiratory ailments such as colds and bronchitis. Its leaves and roots can be prepared as poultices for topical applications, helping with skin irritations or inflammation.
Some practitioners include the dried leaves in herbal remedies aimed at promoting digestion or alleviating pain. It is notable that while skunk cabbage shows promise, caution is necessary due to its alkaloid contents, which can be toxic in high amounts. Research continues into the therapeutic potential of skunk cabbage, providing insights into sustainable use in herbal medicine.
Symbolism in Various Cultures
In various cultures, skunk cabbage carries symbolic meanings as well. The plant is often associated with renewal and resilience, a reflection of its ability to thrive in wetland habitats. In some Native American traditions, skunk cabbage is seen as a symbol of healing, embodying the connection between earth and spirit. Many tribes incorporate it into rituals focused on health and protection.
Furthermore, its unique appearance often evokes curiosity and respect. For example, the strong, distinct odor of skunk cabbage can be considered a lesson in embracing the natural world's oddities. It reminds communities of the diversity of flora and the importance of all species within their ecosystems. This symbolism highlights the importance of skunk cabbage in cultural narratives surrounding nature and wellness.
Skunk cabbage represents both healing and resilience, bridging the gap between traditional practices and modern ecological awareness.
By recognizing these cultural dimensions, one can understand how skunk cabbage is appreciated not only for its biological roles but also for its rich contributions to cultural identity and heritage.
Impacts of Climate Change
Climate change is a pressing issue that affects ecosystems globally, and skunk cabbage is no exception. The impacts of climate change on this unique plant can be divided into two primary categories: shifts in distribution patterns and effects on growth and reproduction. Understanding these aspects is vital for conservation efforts and maintaining ecosystem health.
Shifts in Distribution Patterns
As the climate warms, the geographical range of many plant species, including skunk cabbage, is undergoing significant changes. Generally, skunk cabbage prefers wetland habitats, which are sensitive to climatic fluctuations. Factors such as temperature increase and altered precipitation patterns can lead skunk cabbage to migrate to higher altitudes or latitudes.
This shift in distribution is largely driven by the plant's requirements for specific moisture levels and temperature ranges. In regions experiencing increased drought, the decline of suitable habitats for skunk cabbage could become evident. As it moves, it may also encounter competition from other plant species that expand into these newly accessible environments. The subsequent changes in biodiversity could disrupt existing ecosystems, impacting not only the skunk cabbage but also the wildlife that depend on it.
Moreover, an increase in heavy rainfall events may cause localized flooding, impacting the health of skunk cabbage populations. This loss of habitat can lead to fragmentation, making it difficult for this species to thrive in its traditional ecosystems.
Effects on Growth and Reproduction
The growth and reproductive success of skunk cabbage are closely tied to climate conditions. Warmer temperatures could enable earlier blooming, which may seem beneficial at first glance. However, this can disrupt synchronization with pollinators that have specific life cycles. For instance, if skunk cabbage blooms too early, pollinators such as certain bees may not be active yet, leading to decreased pollination success and lower seed production.
In addition, changes in soil moisture levels can significantly affect root development and nutrient uptake. Skunk cabbage has shallow roots that are susceptible to drought conditions. If water availability decreases, the plant's ability to absorb nutrients is compromised, impacting its overall health. These stressors can also weaken the plant, making it more vulnerable to pests and diseases.
Research indicates that continued climate impacts may lead to reduced reproductive rates, pushing certain populations closer to the brink of local extinction. For forestry professionals and researchers, monitoring these changes is crucial for implementing effective conservation strategies.
Understanding the specific impacts of climate change on skunk cabbage ensures informed decision-making in conservation efforts and ecological management.
Skunk Cabbage in Forestry Practices
Skunk cabbage plays an integral role in forestry practices, particularly in wetland and riparian ecosystem management. Its unique characteristics not only contribute to biodiversity but also enhance the soil health and water quality in forested areas. Understanding the implications of incorporating skunk cabbage into forestry practices enables professionals to create more sustainable environments while promoting the ecological functions that this plant species provides.
Incorporating into Sustainable Forestry
Incorporating skunk cabbage into sustainable forestry methods can yield significant advantages. This plant thrives in wet or waterlogged conditions, often found in forest understories. By including skunk cabbage in forestry planning, land managers can improve the habitat for various wildlife species, including amphibians and birds, that depend on wetland plants for shelter and food. The dense growth of skunk cabbage also contributes to natural flood control by absorbing excess water, reducing the risk of erosion in forested areas.
- Ecosystem Services: Skunk cabbage offers vital services such as water filtration and nutrient cycling. As a primary producer in the ecosystem, it assists other plants by improving soil quality.
- Biodiversity Support: Enhancing habitats with a variety of native plants, including skunk cabbage, fosters a richer ecosystem. More biodiversity contributes to ecosystem resilience.
- Climate Adaptation: Increasing the presence of skunk cabbage may help forests adapt to climate change through improved water retention and enhancing nitrogen levels in the soil.
The application of skunk cabbage in forestry may not be conventional, yet it presents a beneficial opportunity for land managers to synergize plant life with environmental stability.
Conservation Strategies
Effective conservation strategies are essential for ensuring the ongoing presence of skunk cabbage in forests. Protecting its habitat is critical, as this plant relies on specific wetland conditions. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Habitat Preservation: Maintaining existing wetland areas is crucial. Limiting drainage or development in these habitats helps preserve the natural ecosystems where skunk cabbage thrives.
- Restoration Projects: Initiating restoration projects in degraded wetlands can reinstate conditions favorable to skunk cabbage, along with other native species. Restorative approaches promote ecological balance.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts can raise awareness about the ecological importance of skunk cabbage. Educational programs highlighting its benefits can lead to greater community support.
- Monitoring and Research: Continuous research and monitoring of skunk cabbage populations allow for timely interventions. Understanding its growth patterns and reproductive ecology aids in developing effective management practices.
Conserving skunk cabbage not only benefits the species itself but also enhances overall forest health and resilience.
In summary, skunk cabbage has significant implications for forestry practices. By incorporating this unique plant, professionals can foster sustainable forest ecosystems that are beneficial for both biodiversity and soil health. Ultimately, the foresight to include skunk cabbage in forestry management reinforces the intricate connections within wetland and forest ecosystems.
Interactions with Other Flora and Fauna
Skunk cabbage plays a significant role in its ecosystem, particularly through its interactions with other plants and animals. Understanding these interactions is crucial for appreciating its ecological value. The relationship of skunk cabbage with surrounding flora and fauna encompasses symbiotic relationships and the impacts of invasive species.
Symbiotic Relationships
Skunk cabbage has various symbiotic relationships within its habitat. One of the most notable interactions is with pollinators, particularly flies and certain beetles. The unique flowers of skunk cabbage emit a smell that mimics decaying organic matter. This odor attracts these pollinators, which are essential for the plant's reproductive process. When these insects come to the flower, they facilitate pollination, allowing for successful seed production.
Additionally, skunk cabbage provides a habitat for various microorganisms that may enhance nutrient availability in the soil. Mycorrhizal fungi, which form associations with the roots of skunk cabbage, help the plant absorb moisture and nutrients from the soil. This relationship benefits both the fungus and the skunk cabbage, illustrating a mutual exchange that promotes growth and ecosystem stability.
Invasive Species Considerations
Despite the ecological importance of skunk cabbage, it can face threats from invasive species. Non-native plants may outcompete skunk cabbage for resources like light, water, and nutrients, leading to a decline in skunk cabbage populations within its habitat. For example, species such as garlic mustard can spread rapidly and create dense monocultures that choke out native flora, including skunk cabbage.
The introduction of invasive species can alter the delicate balance of the ecosystems where skunk cabbage thrives. Moreover, invasive animals that disrupt vegetation, such as deer, can also negatively impact skunk cabbage populations by feeding on its leaves and flowers. Effective management practices need to be considered to mitigate these threats and protect the ecological integrity of wetland ecosystems.
"Skunk cabbage serves as a critical component of its ecosystem, but the presence of invasive species threatens its survival and the health of wetland environments."
In summary, the interactions of skunk cabbage with other flora and fauna underline its ecological significance. Its relationships with pollinators and beneficial fungi underscore the importance of maintaining biodiversity in its habitat. However, challenges posed by invasive species highlight the need for ongoing conservation efforts. Understanding these dynamics is essential for forestry professionals and academics involved in ecosystem management.


Research and Studies
Research on skunk cabbage is crucial in understanding its ecological significance and the broader impacts it has in wetland environments. This section focuses on various aspects of research including current scientific studies and historical findings that shed light on the plant's role in its ecosystem.
Current Scientific Research
Recent scientific endeavors have brought to light the multifaceted role of skunk cabbage in wetland ecosystems. Ongoing studies emphasize how skunk cabbage contributes to nutrient cycling within wetland habitats. Researchers examine its ability to uptake nutrients, thus helping to maintain the ecological balance. For example, studies show that skunk cabbage can absorb excess nitrogen and phosphorus, which are often detrimental in elevated concentrations.
Furthermore, investigations are being conducted on the plant's adaptation to climate change. Understanding how fluctuating temperatures and varying moisture levels affect growth patterns is vital for conservation efforts. Research indicates that skunk cabbage displays remarkable resilience against environmental stressors, which may serve as an indicator species for assessing ecosystem health.
Among the most prominent research projects are those involving the interactions between skunk cabbage and its pollinators. Observations detail how the flower structure and scents attract specific fauna, thus reinforcing its role in supporting biodiversity in its natural habitat.
Historical Studies and Findings
The historical context of skunk cabbage research dates back several decades, with early studies primarily focused on its taxonomy and morphology. Botanists like John M. S. Campbell have contributed significantly to the foundational understanding of the species, classifying it under the Symplocarpus genus. These early classifications laid the groundwork for specialized research in later years.
Notably, some historical studies have highlighted the plant's medicinal uses among native cultures. Ethnobotanical research provides records illustrating how Indigenous peoples utilized skunk cabbage for various ailments, embracing its natural properties. These findings are crucial in understanding the cultural dimensions of the species.
It is also essential to consider the evolutionary studies conducted on skunk cabbage. Research during the 1970s explored how geological and environmental factors influenced its current distribution. Such studies reveal patterns of adaptation that have enabled skunk cabbage to thrive in specific wetland ecosystems.
Conservation Challenges
Conservation challenges regarding skunk cabbage encompass a range of issues that threaten its survival and the integrity of its habitats. As this plant plays a significant role in wetland ecosystems, understanding these challenges is crucial to preserving both skunk cabbage and the ecological balance it supports. The preservation of this species is not just essential for its own sake, but also for the wildlife and other plants that depend on these habitats.
Threats to Habitat Quality
The quality of skunk cabbage habitats is under threat from multiple sources. Urban development is one major factor. As cities expand, wetlands are drained or filled. This destroys the unique environments that skunk cabbage requires for growth. Water pollution is another issue. Runoff from agricultural areas often contains fertilizers and pesticides. These chemicals can degrade water quality in wetlands, negatively affecting skunk cabbage growth and the health of the ecosystem.
Natural events also pose risks. Changes in rainfall patterns or prolonged droughts can alter the sensitive hydrology of these ecosystems. Skunk cabbage thrives in moist conditions. Insufficient water can inhibit its growth, causing declines in local populations. Additionally, the spread of invasive species often disrupts the balance of plant and animal life, overshadowing native flora like skunk cabbage and pushing it out of its niche.
- Urbanization leads to habitat loss.
- Pollution has direct toxic effects.
- Climate extremes can modify wetland hydrology.
- Invasive plants can dominate areas where skunk cabbage grows.
Policy and Regulation Issues
Regulatory frameworks must evolve to address the pressing conservation challenges faced by skunk cabbage. Policies often lag behind the current scientific understanding of the ecological dynamics in wetlands. Land use policies can be especially detrimental if they do not prioritize the protection of wetland ecosystems. Without clear regulations, developers can exploit these areas without consideration for the environmental impacts.
Additionally, existing conservation laws may not adequately cover the specific needs of skunk cabbage and its habitat. Strengthening legislation related to wetland preservation is essential.
The implementation of preservation strategies can include:
- Establishing protected areas to limit development.
- Enhancing pollution controls and enforcing regulations on agricultural runoff.
- Raising public awareness about skunk cabbage's ecological significance.
Resources such as the Environmental Protection Agency and local conservation organizations play vital roles in advocating for necessary changes to existing policies.
It is crucial that we recognize the interconnectedness of ecosystems in any conservation strategy aimed at protecting skunk cabbage and its habitat.
Future Directions
Understanding the future of skunk cabbage is essential for its conservation and ecological management. As climate change and habitat degradation threaten wetlands, proactive measures must be considered. This section explores advocacy for skunk cabbage protection and innovative conservation approaches that may help safeguard this plant and its ecosystem.
Advocacy for Skunk Cabbage Protection
Advocacy plays a critical role in protecting skunk cabbage. Organizations and individuals can rally support for various initiatives. This can include the promotion of legislation aimed at preserving wetland habitats. When local communities understand the ecological importance of skunk cabbage, they are more likely to support conservation efforts.
Protecting skunk cabbage requires a comprehensive approach. Here are some strategies that can be adopted:
- Educational Campaigns: Inform the public about the ecological benefits of skunk cabbage.
- Workshops and Seminars: Engage communities in discussions about conservation strategies.
- Collaboration with Local Governments: Work to integrate skunk cabbage protection into environmental planning.
Innovative Conservation Approaches
Innovative conservation approaches are necessary as traditional methods may not suffice in addressing current challenges. Here are some significant considerations in future conservation strategies for skunk cabbage:
- Restoration Projects: Initiate projects to rehabilitate degraded wetland areas favorable to skunk cabbage growth.
- Research and Monitoring: Develop ongoing research programs to monitor the health of skunk cabbage populations and their habitats.
- Citizen Science: Empower local citizens to participate in data collection and monitoring of skunk cabbage conditions.
In essence, a combination of advocacy and innovative approaches can create a robust framework. This framework ensures that skunk cabbage remains a vital part of wetland ecosystems for future generations. Collaboration among environmental groups, academia, and local governments is crucial in these efforts.
"Conservation is a state of harmony between men and land." - Aldo Leopold
By engaging with these strategies, stakeholders can ensure the continued survival of skunk cabbage, emphasizing its ecological significance.
Culmination
The conclusion is a crucial part of any comprehensive overview, providing clarity on the significance of the topic discussed. In this article, we touched upon various aspects of skunk cabbage, its ecological roles, and interactions within wetland ecosystems. Summarizing these elements allows readers to grasp the multi-faceted importance of this unique plant. Each section of the article contributes to a broader understanding of skunk cabbage and its intricate place in nature.
One important element discussed is the plant's contributions to habitat stability. Skunk cabbage establishes a solid foothold in wetland areas, assisting in controlling soil erosion. Additionally, it serves as a vital food source for certain wildlife that depend on it during early spring when other food sources are scarce.
Considering the ecological implications, it is necessary to highlight the broader context of conservation challenges faced by this plant. Awareness around such topics helps in the formulation of strategies that can aid in maintaining the delicate balance of wetland ecosystems. Overall, the conclusion synthesizes the information provided and emphasizes the importance of acknowledging skunk cabbage as not just a biological entity but as an essential component of its habitat.
Summary of Key Points
- Skunk cabbage plays a significant role in wetland ecosystems by providing food and habitat for various species.
- Its unique adaptations allow it to thrive in wet environments, contributing to soil stabilization and moisture retention.
- The plant has historical and cultural uses, especially in traditional medicine.
- Climate change poses risks to its distribution and overall health, necessitating a closer examination of its future viability.
Call for Further Research and Action
Further research on skunk cabbage is necessary. It is vital to explore its adaptive characteristics and the potential effects of climate change on its growth and reproduction. Understanding these factors can guide conservation efforts, ensuring that skunk cabbage and similar species thrive in their natural habitats. Conservation strategies should include monitoring population health and advocating for wetland preservation.
Scientists, conservationists, and policymakers need to collaborate to develop a comprehensive approach to protect wetland ecosystems and the species that rely on them. Engaging with communities and educating the public about the significance of skunk cabbage could also foster greater appreciation and protection of these vital ecosystems.
In summary, skunk cabbage offers considerable ecological significance. To ensure that this unique plant continues to flourish within its environments, ongoing study and proactive measures are crucial.







