Exploring Birch Bark Paper: Nature's Artistry Unfolded


Intro
Birch bark paper is more than just a medium; it's a canvas that embodies the unity between artistry and the natural world. As we embark on the journey of exploring this distinctive form, we will discover not only its history and cultural significance, but how it serves as a testament to the delicate balance of our woodland ecosystems. This unfolding narrative speaks to those who cherish nature's raw beauty and recognize the craft that goes into transforming bark into breathtaking art.
Understanding Woodland Ecosystems
Importance of Biodiversity in Forests
Forests are intricate webs of life, each species contributing to the overall health and function of the ecosystem. Biodiversity plays a pivotal role here, ensuring resilience against diseases and climate shifts. A robust forest, rich in various species, maintains soil quality, promotes water retention, and enhances air quality. The birch tree, which serves as the primary source for birch bark paper, thrives in diverse woodland settings, which in turn supports an entire ecosystem.
Role of Forests in Climate Regulation
Forests act as lungs for our planet by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. The process of photosynthesis is vital not just for the trees but for all life forms. A well-managed forest helps regulate local climates and mitigate the effects of extreme weather. In the context of birch bark paper, sustainable harvesting practices allow artisans to draw upon this natural resource while maintaining the health of the forest.
Sustainable Forestry Practices
Principles of Sustainable Forestry
Sustainable forestry focuses on using forest resources in a manner that meets current needs without compromising future generations. Here are some tenets of sustainable forestry that are especially pertinent to birch bark harvesting:
- Selective Harvesting: Only the necessary amount of bark is removed from the tree, allowing it to heal and continue growing.
- Ecosystem Preservation: Maintaining habitats for various species promotes biodiversity and enhances ecological stability.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in the decision-making process ensures that practices align with cultural traditions and economic needs.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Examples abound where communities have successfully implemented sustainable practices. The Gwich’in people have long engaged in the mindful harvesting of birch bark, ensuring that it continues to be a viable resource for generations. These practices demonstrate that with care, both culture and nature can coexist harmoniously, fostering an environment where birch bark paper can thrive.
Woodland Stewardship Techniques
Forest Management Plans
Having a solid forest management plan is crucial for sustainable birch bark harvesting. These plans typically involve:
- Assessing the current state of the forest.
- Setting clear goals for conservation and resource use.
- Monitoring progress regularly to adaptively manage the forest's health.
It's essential to balance the needs for artistic expression with ecological stewardship so that future generations can also enjoy this remarkable resource.
Conservation Strategies
Conservation strategies can be as diverse as the ecosystems they aim to protect. Some key approaches include:
- Replanting Efforts: Ensuring that areas harvested for birch bark are reforested with the same species.
- Public Education: Raising awareness about the significance of birch bark and its integration within cultural practices.
- Research and Development: Encouraging studies that investigate the long-term impacts of bark harvesting on tree health and forest composition.
"The essence of birch bark paper reflects our intrinsic connection to nature, showing that with wisdom, we can honor and utilize it without depletion."
This narrative sets the stage for a profound exploration into birch bark paper, revealing its layers as both an art form and a sustainable practice deeply rooted in indigenous culture and ecological balance. As we peel back these layers, we will uncover the beauty and craftsmanship involved in creating this natural art form.
Foreword to Birch Bark Paper
Birch bark paper is more than just a medium; it embodies a confluence of tradition and craftsmanship that has been passed down through generations. For forestry professionals and academics alike, understanding this unique paper form is crucial for grasping how ecological practices, art, and cultural significance intertwine. This topic underscores the relationship between nature and human creativity, drawing attention to the sustainable methodologies that can be employed in art and conservation.
In this section, we will explore the definition and characteristics of birch bark paper, setting the stage for deeper discussion on its history and cultural relevance.
Definition and Characteristics
Birch bark paper is created from the outer bark of birch trees, primarily the paper birch (Betula papyrifera). The paper has a distinct appearance—its surface displays a unique mosaic of natural shades, offering a tactile and visual palette that is seldom found in synthetic papers.
One of the most striking characteristics of birch bark paper is its durability. Unlike standard paper, it has a fibrous structure that is both flexible and tough, which enables it to withstand wear over time. The natural oils present in the bark can give the paper a slight sheen, enhancing its aesthetic appeal for artistic applications.
When discussing defining features, it’s also essential to mention its eco-friendly nature. As birch trees are renewable resources when harvested responsibly, the process of making birch bark paper emphasizes sustainability—a principle that is becoming more vital in today’s environmentally-conscious society. Additionally, the paper can be dyed and treated using natural pigments, further aligning with ecological ideals in art.
Historical Background
The roots of birch bark paper trace back centuries, particularly within Indigenous communities of North America. Historically, the use of birch bark for making paper and crafts was not merely practical; it was also spiritual and ceremonial. Indigenous peoples, such as the Ojibwe and Cree, utilized birch bark in various aspects of life, from writing sacred texts to creating complex visual art forms.
"Birch bark represents a tapestry of traditions, resilience, and connection to the land."
This craft flourished as it became a crucial tool for storytelling and communication. Early explorers and settlers were introduced to this paper, observing how the native populations valued it for both its utility and beauty.
Over time, birch bark paper has transitioned from a survival tool to an esteemed art form, often regarded as a showcase of meticulous craftsmanship. The historical narrative around birch bark paper highlights not only the ingenuity of its makers but also how cultural narratives are woven into the physical fabric of the medium itself.
The understanding of birch bark paper, both in its characteristics and historical context, sets a robust foundation for further exploration into its cultural significance and crafting processes. By engaging with the traditions tied to birch bark paper, we can appreciate its contemporary applications and the continuing role it plays in honoring our natural world.
Cultural Significance
Birch bark paper carries profound cultural significance, especially among Indigenous communities. This natural medium is more than just a canvas or surface for artistic expression; it symbolizes generations of tradition and connection to the land. Through birch bark paper, various cultural narratives and knowledge are preserved, making it a vital element of heritage.

Indigenous Practices
The craftsmanship surrounding birch bark paper is deeply rooted in the practices of Indigenous peoples in North America and parts of Asia. Historically, birch trees were revered not only for their physical utility but also for their spiritual importance. The act of harvesting birch bark is imbued with traditions, where the tree is treated with respect. Practitioners often engage in ceremonies before gathering, emphasizing gratitude for the resources nature provides.
Traditional uses of birch bark paper include:
- Craft Making: Native artisans create various objects like baskets and clothing.
- Storytelling: Artists often inscribe stories or cultural teachings onto the paper, passing down knowledge through visual art.
- Ritualistic Items: The material serves in crafting items for spiritual ceremonies, linking the physical and spiritual worlds.
The process of crafting with birch bark is a communal activity as well. Families and tribes often come together to share techniques, therefore fostering a sense of community and collective historical awareness. The wisdom imparted from one generation to another helps keep vital cultural practices alive.
This intertwining of artistry and utility not only highlights the skills involved but also underlines the importance of sustainability. The practices emphasize the need to harvest in a way that maintains the birch population, teaching younger generations about stewardship of the land.
Art and Spirituality
The significance of birch bark paper transcends mere artistic pursuits; it manifests as an entry point into the spiritual realm. Many Indigenous cultures view the act of creating art from natural materials as a spiritual endeavor. Each piece tells a story, offering insights into the broader cosmos and the relationships between people and nature.
Artworks crafted on birch bark often reflect themes of identity, community, and the interconnectedness of all living things. The textures and colors inherent in the bark itself can evoke images of nature, which artists often incorporate into their work.
Quote from a prominent Indigenous artist:
"When I work with birch bark, I am not just creating art; I'm weaving my lineage into a tangible form that speaks to my ancestors and to the earth."
The emphasis on spirituality can also serve as a counter-narrative to modern perceptions of art as mere decoration or consumerist product. Artists often share their process, emphasizing the care and thought that goes into their creations, rather than just the final product. This level of intention encourages deeper connections, encouraging viewers and participants to engage with the pieces on multiple levels.
In summary, the cultural significance of birch bark paper is multifaceted, blending artistry, tradition, and spirituality into a rich tapestry of communal history and ongoing environmental stewardship. The ongoing practice of creating birch bark art can serve as a powerful reminder of the interdependence between culture and nature, emphasizing that the act of creation is just as important as the creation itself.
The Crafting Process
The crafting process of birch bark paper represents a harmonious blend of artistry and nature. This meticulous practice not only highlights the importance of birch trees in communities but also underscores the ecological relationship between humans and the environment. When artisans engage in this intricate process, they are not merely creating a product; they’re participating in a time-honored tradition, preserving cultural heritage while promoting sustainability.
Among the core elements are harvesting, preparing, and creating the paper itself. Each stage plays a significant role in determining the quality and character of the final product.
Harvesting Birch Bark
Seasonal Considerations
The timing of harvesting birch bark hinges heavily on seasonal cycles. Particularly, the spring months provide an optimal window for birch bark collection. During this period, the sap begins to flow, causing the bark to separate more easily from the cambium layer, making it less likely to harm the tree.
A key characteristic of this timing is that it adheres to traditional practices passed down through generations among indigenous communities. Its advantage lies not only in facilitating a smooth harvesting process but also in ensuring that the tree can recover fully post-harvest. This method can be beneficial as it supports the health of birch populations and therefore sustains the craft itself.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is critical when it comes to collecting birch bark. Sustainable practices involve ensuring that harvesting does not lead to the depletion of birch trees. Stripping too much bark from one tree can greatly affect its health, so artisans often take only a thin layer.
The most pronounced feature in this regard is the intergenerational knowledge that advocates for tree health, guiding artisans in their methods. Given it promotes ecological balance, this approach not only preserves the resource for crafting birch bark paper but also benefits the broader surroundings—creating a beneficial tie between culture and conservation.
Preparing the Bark
Cleaning Techniques
Once the bark is harvested, it undergoes a thorough cleaning. The cleaning techniques used typically include soaking the bark in water to remove dirt, debris, and any loose layers. This is crucial as any remnants or impurities could affect the integrity of the final paper.
By employing methods that are often natural, such as using only water or minimal eco-friendly detergents, artisans emphasize the respect for the materials they work with. This practice can also be perceived as a rite, further linking the artist with the natural world.
Cutting and Shaping
Cutting and shaping the bark into desired pieces come next. Here, precision is vital. Part of the artistry involves knowing how to approach the bark to yield various sizes according to the intended use. Techniques often reflect the artist's preference and might include using sharp knives or even simple scissors.
This manipulation of the material allows for creativity to unfold. However, missteps in cutting can lead to wastage of this precious resource. A careful, respectful approach here means a better outcome overall and promotes the wise use of natural materials.
Creating the Paper
Layering Methods
In building the actual paper, layering methods become paramount. Artisans typically overlap layers of birch bark, each layering adding texture and strength. This technique not only enhances the durability of the final product but also introduces a distinct aesthetic, often marked by the unique patterns of the bark itself.
Such methods also foster artistic expression, giving creators the freedom to experiment with the weight and feel of the paper.
Drying and Finishing
After layering, the paper must be dried properly. This step solidifies the bond between the layers and ensures the final product maintains both functionality and beauty. The drying process may take place in well-ventilated areas where the circulation of air facilitates even drying, avoiding mold or warp.
Finishing touches may include trimming the edges or applying natural oils for sheen, providing not just an elegant look but also extra protection. The choice of these techniques can greatly influence the visual appeal and functional quality of the birch bark paper, emphasizing that every step feeds into the overall craftsmanship.
"Crafting birch bark paper is not just about the end product; it is an enduring dialogue between the artisan and the natural world."
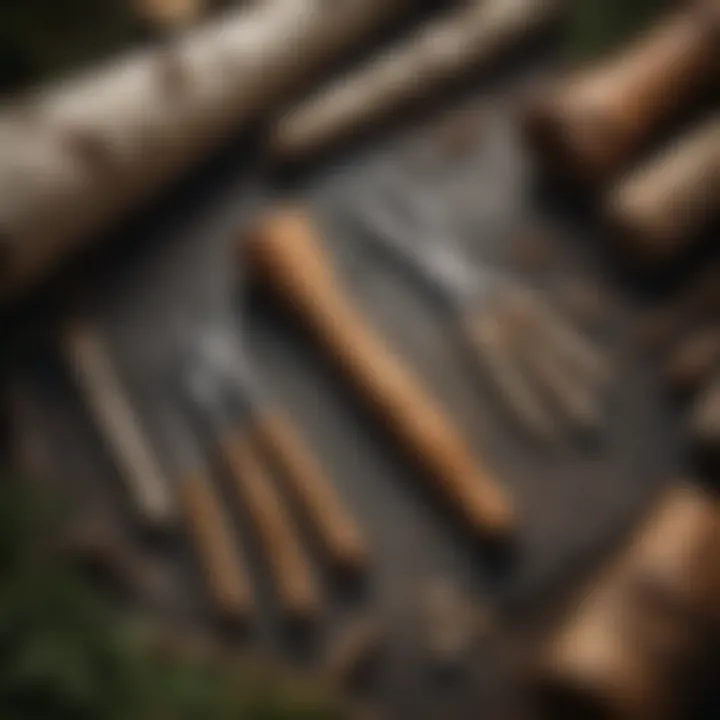


In summary, the crafting process of birch bark paper is not merely a series of steps but an intricate pattern of cultural respect, sustainability, and creativity. Each aspect plays a pivotal role in ensuring the future of this remarkable natural art form.
Applications of Birch Bark Paper
Birch bark paper, steeped in tradition and crafted with care, finds its footing in a variety of applications that stretch across both artistic and educational realms. Its importance in this discourse revolves around how it serves as a medium not only for creative expression but also as a tool for learning and cultural preservation. As the world increasingly turns its gaze toward sustainable practices, the relevance of birch bark paper is underscored by its ecological benefits and cultural heritage.
Artistic Uses
Traditional Crafting
Traditional crafting with birch bark paper offers a window into ancestral practices that honor nature while producing exquisite art. In many Indigenous cultures, artisans utilize birch bark to create items such as baskets, containers, and ceremonial objects. The flexibility and strength of the bark—which can be shaped by hand without losing its integrity—are key characteristics that make it an ideal choice. For artists, traditional crafting is celebrated for its organic aesthetic and deep cultural resonance.
One unique feature of traditional crafting is the storytelling inherent in each piece, often reflecting specific narratives or connection to the land. However, it does carry challenges such as the need for specific skills and the time-consuming nature of crafting, which can deter some modern artists.
Modern Art
In contrast, modern artists embrace birch bark paper as a means to push boundaries and experiment with mixed media. Its rich texture and natural hues create a unique backdrop for contemporary works, allowing artists to blend traditional techniques with modern aesthetics. A pivotal characteristic of modern art using birch bark is its ability to inspire dialogue on sustainability and the material's role in environmental art.
The uniqueness of modern art pieces lies in their innovative creations—installations, collages, and sculptures—that convey messages about nature and conservation. However, the challenge can be in audience reception; critics may not always understand the amalgamation of traditional materials with new artistic visions.
Educational Value
Workshops and Classes
Workshops centered around birch bark paper crafting serve an essential role in transferring knowledge about this traditional practice. These sessions provide hands-on experience, bridging generations by teaching techniques passed down through years. The key characteristic of such workshops is their immersive nature, where participants engage directly with the material.
Notably, the workshops foster a community of learners and artisans, enhancing appreciation for Indigenous cultures and ecological mindfulness. Nevertheless, they may require careful planning and skilled instructors to ensure authenticity and effectiveness.
Resource for Teachers
The utilization of birch bark paper as a resource in educational settings opens pathways for discussing environmental stewardship and cultural heritage. Teachers can integrate lessons around birch bark into subjects such as art, history, and ecology. Its key characteristic lies in its multifaceted approach, covering both artistic techniques and ecological education.
A distinctive feature for educators is the opportunity to inspire creativity while fostering respect for natural resources. However, reliance on this resource might be limited by access to materials and the necessary prior knowledge to handle such traditional crafts effectively.
Exploring the various applications of birch bark paper reveals its dual role as an artistic medium and an educational tool, enriching both individual expression and communal knowledge.
Ecological Considerations
Understanding the ecological considerations surrounding birch bark paper is vital, not just for the art form but also for the sustainability of forests. This paper-making process is intertwined with the life cycles of birch trees, which have unique roles within their ecosystems. From the harvesting methods employed to the conservation efforts in place, these factors collectively paint a broader picture of how birch bark paper production can harmonize with nature.
Sustainability of Birch Trees
Impact of Harvesting
The impact of harvesting birch bark is a double-edged sword. On one hand, responsibly collecting bark allows artisans to create this traditional paper, showcasing its unique texture and natural beauty. On the other, if done carelessly, it can threaten the very trees that provide this resource. Selctive harvesting practices have proven to be beneficial; they allow trees to regenerate their bark over time while safeguarding the health of birch populations. Advances in sustainable practices encourage not only the maintenance of a steady supply of bark but also the preservation of forest integrity.
The key characteristic of such sustainable practices lies in their emphasis on minimal impact. Harvesting birch should occur during specific seasons to support tree health and growth. This method ensures that the trees can recover efficiently, allowing artisans to harvest bark in a way that is both sensitive to environmental needs and beneficial for making high-quality paper. The unique feature of controlled harvesting is its balance—maximizing the yield of birch bark while simultaneously preserving the species.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts in relation to birch trees have gained traction as communities become more aware of the ecological issues facing their environments. Techniques such as reforestation play a significant role in ensuring that birch populations remain resilient amid threats from climate change and urban development. Education and awareness campaigns illuminate the critical needs of birch ecosystems, urging locals to advocate for and engage with conservation initiatives.
A crucial aspect of these efforts is community involvement. It fosters a sense of stewardship that extends beyond the singular act of harvesting. The unique feature of such conservation strategies is their dual benefit; they not only support the birch trees but also educate the community about the importance of forest conservation. In doing so, these strategies enhance the ecological balance while ensuring that future generations can continue to enjoy the artistry of birch bark paper.
Biodiversity and Habitat
Birch trees are not just beneficial for making paper; they also serve as essential components in forest ecosystems. This section examines how the role of birch trees supports biodiversity and habitat stability.
Role of Birch in Forest Ecosystems
The role of birch trees within forest ecosystems is significant. They improve soil quality, which in turn supports a broader range of plant species. As pioneer species, birches are often the first trees to colonize damaged or disturbed land. Their growth creates conditions for other plants to thrive, thus increasing biodiversity. Furthermore, birches provide important habitat for various insects and birds, contributing to a rich tapestry of life that thrives within these forests.
This characteristic makes birch trees incredibly valuable in maintaining ecological balance. When birch trees flourish, they not only enrich their immediate environment but also help towards the sustainability of the forest as a whole. Their unique adaptability allows them to thrive in a range of conditions, making them a vital part of forest regeneration efforts.
Supporting Wildlife
Supporting wildlife is another critical function of birch trees. They offer shelter and food for various species, including birds, insects, and mammals. For example, the bark can be a source of nesting material for birds, while the leaves serve as food for many insects. These interactions highlight how birch trees play an important role in sustaining wildlife populations.
A key characteristic of birch trees is their ability to provide not just for themselves but for other life forms around them. Their unique contribution to supporting wildlife is multifaceted—acting as both habitat and sustenance. As a keystone species, birches ensure a more stable and vibrant ecosystem, which is crucial for maintaining plant and animal diversity.
The intertwining of birch trees and their ecosystems is a subtle reminder that every element in nature serves a purpose, whether as a source of art or as a provider of life.
Challenges and Preservation
In our exploration of birch bark paper as a natural art form, the conversation naturally gravitates towards the challenges faced in preserving this unique material and the ecosystems from which it springs. As we delve into the intricate relationship between birch trees and their environments, we must confront the pressing issues that threaten both the sustainability of birch bark paper and the trees themselves. Understanding these challenges is crucial not only for artists but also for conservationists and forestry professionals.
Threats to Birch Populations
Climate Change
Climate change plays a significant role in the challenges confronting birch trees. These trees, known for their delicate bark and valuable resources, face shifting weather patterns that render their habitats more inhospitable. One key characteristic of climate change is its unpredictability. Wildfires, severe storms, and unseasonable temperatures can wreak havoc on birch populations. This unpredictability can be detrimental to the health of forest ecosystems where birch trees thrive. Continual stress from changing climates often leads to diminished bark quality, which directly impacts the viability of birch bark paper as an art medium.
Additionally, shifts in temperature and moisture levels create optimal conditions for pests that target birch trees. The presence of the bronze birch borer, for example, has increased significantly in areas experiencing climate shifts. This pest can cause extensive damage, weakening trees and ultimately leading them to succumb to other environmental stresses.


Deforestation
Deforestation constitutes another significant threat to birch populations. Urban expansion, industrial logging, and agricultural development have caused forests to dwindle, snuffing out the habitats crucial for birch trees. The key characteristic of deforestation lies in its rapid pace, leaving little room for natural regeneration. Once a forest is cleared, the intricate ecosystem can't easily bounce back. This disruption stifles not only birch trees but also countless other species that rely on those forests for survival.
Moreover, the loss of birch trees translates directly into the declining availability of birch bark—a material intertwined with cultural heritage and artistic expression. When deforestation occurs, it also reduces the spaces where people can harvest birch sustainably, further eroding the traditions associated with birch bark paper crafting.
Conservation Strategies
Reforestation Efforts
Reforestation efforts stand as a beacon of hope amid the looming threats to birch tree populations. This practice involves planting native trees in areas where forests have diminished, aiming to restore ecological balance and biodiversity. A unique feature of reforestation is its dual focus—while it repairs damaged ecosystems, it also nurtures the potential for sustainable harvesting of birch bark in the future. In this sense, reforestation emerges as a beneficial choice, promising to revive birch populations and ensure the continued existence of birch bark paper crafting.
However, reforestation must be approached thoughtfully. Planting the right species in the right locations is essential, as introducing non-native species could exacerbate existing issues, further pushing local ecosystems out of balance.
Community Initiatives
Community initiatives play a vital role in the conservation of birch tree populations. These grassroots movements are born from local residents recognizing the intrinsic value of their natural resources. A key characteristic of community initiatives is their emphasis on collaboration; people come together to educate, conserve, and advocate for their local forests. This can include organizing awareness campaigns, holding workshops on sustainable practices, and establishing tree-planting events. By fostering a sense of ownership in the local environment, these initiatives can significantly contribute to preserving birch trees for future generations.
The uniqueness of community initiatives lies in their capacity to engage a wide array of stakeholders. It’s not only about artists and conservationists but also includes schools, local businesses, and even policymakers. When communities band together for a common purpose, they create a powerful force that promotes both environmental stewardship and appreciation for the delicate craft of birch bark paper making.
Saving our birch populations is not just the work of one; rather, it's a symphony played best in harmony.
In summary, addressing the challenges surrounding birch trees involves a multi-faceted approach that includes understanding threats like climate change and deforestation, while actively engaging in reforestation and community initiatives. Each effort contributes to a future where birch bark paper can continue to be a cherished medium for artists and an integral component of our natural heritage.
Future of Birch Bark Paper
The journey of birch bark paper is far from over. As we navigate through an era marked by ecological consciousness and a renewed appreciation for natural materials, the future of birch bark paper presents both opportunities and challenges. This section dives into innovative applications and the growing wave of sustainability practices, positioning birch bark paper not just as an art form but as a medium adaptable to modern needs.
Innovative Uses
New Artistic Mediums
Exploring birch bark paper as a new artistic medium opens up a world of creative possibilities. Artists and crafters are increasingly turning to this organic material not only for its aesthetic qualities but also for its environmental benefits.
One significant feature of using birch bark paper is its distinctive texture and patterning, which can enhance visual storytelling in various art forms. The natural lines and flecks of the bark can complement and even amplify the artistic narratives.
This innovative use allows for a more sustainable practice, aligning with the preferences of a contemporary audience that values eco-friendly materials. However, it does present some challenges. Working with birch bark paper can require a learning curve, especially in terms of achieving desired effects without compromising the integrity of the medium.
Collaborative Projects
The aspect of collaborative projects in birch bark paper artistry cannot be overstated. When artists come together to explore this medium, they blend diverse techniques and cultural insights, contributing to a rich, evolving art scene.
Collaborative initiatives can serve as a springboard for community engagement, making birch bark paper accessible to a broader audience. This approach emphasizes not only creativity but also the idea of shared learning and resourcefulness. However, one must consider the coordination required to maintain such partnerships, which can sometimes lead to logistical challenges.
Growing Interest in Sustainability
Market Trends
As consumers become more environmentally aware, market trends show a notable shift towards sustainable products, including birch bark paper. This growing interest reflects a broader societal movement that values ethical sourcing and low-impact materials.
Investing in birch bark paper aligns well with these market demands, as it directly relates to both sustainability and artistry, promoting a narrative that resonates with modern consumers. Yet, businesses involved must navigate competition and ensure that they communicate the value of their sustainable offerings effectively.
Educational Outreach
Educational outreach plays a pivotal role in popularizing birch bark paper. Workshops, lectures, and hands-on demonstrations let enthusiasts learn about the history, crafting techniques, and ecological implications of this ancient medium.
Not only does this enhance appreciation for the art form, it also cultivates a community invested in sustainable practices. While educational outreach can take various forms, including online classes or in-person workshops, it does require resources and commitment from educators and organizations alike.
"Birch bark paper symbolizes not just creativity but a commitment to sustainable practices that reverberate through communities."
The future of birch bark paper looks promising, filled with potential innovations and a growing constituent of people who care about how their art interacts with the world around them. Through collaboration, education, and artistic exploration, this medium has the opportunity to thrive, creating a lasting impact on both the art community and the environment.
The End
In wrapping up the exploration of birch bark paper, it's essential to reflect on its multifaceted significance. This natural art form isn't just about creating something beautiful; it embodies a unique intersection of history, culture, sustainability, and artistic expression. From the indigenous communities that pioneered its use to the contemporary artists who breathe new life into this ancient craft, birch bark paper serves as a testament to human creativity and our intrinsic connection to nature.
Summary of Insights
Throughout this article, we've traversed various dimensions of birch bark paper.
- Historical Context: The roots of birch bark paper are deeply entrenched in the traditions of indigenous peoples. It was utilized for diverse purposes—ranging from artistic creations to practical uses in daily life.
- Crafting Process: The journey from tree to finished product involves meticulous harvesting, preparation, and crafting techniques. It's a laborious process that emphasizes respect for the environment and the birch tree itself.
- Cultural and Ecological Importance: Understanding the cultural significance furthers recognition of the paper's ecological role, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices in its production.
- Future Prospects: As interest in eco-friendly artistry grows, birch bark paper stands at the forefront of innovative artistic mediums. Its adaptability assures continued relevance in both art and educational realms.
In summation, birch bark paper is not merely a crafting material but a bridge between tradition and modernity, a symbol of respect for the earth, and a canvas for creativity that invites exploration and understanding.
Call to Action
As we contemplate the future of birch bark paper and its applications, it’s crucial for readers—especially forestry professionals and academics—to consider actively engaging with this medium. Here are a few suggestions:
- Support Local Artisans: Purchase birch bark paper items from local artisans or consider commissioning bespoke pieces. This ensures a sustainable practice while promoting community craftsmanship.
- Participate in Workshops: Join workshops focusing on birch bark paper crafting. These events can provide hands-on experience and a deeper appreciation of the skills involved.
- Raise Awareness: Utilize social media platforms such as Facebook and Reddit to share insights and foster discussions about the significance of birch bark paper.
- Conduct Research: For academics, research into the ecological impacts and historical relevance of birch bark can contribute to broader dialogues about sustainability and heritage.
Engaging with birch bark paper is a way to honor its rich history and promote its future viability. This ethos of stewardship isn't just a nice thought—it's an imperative for our shared environment.







