A Detailed Look at the Dwarf Red Buckeye Tree


Intro
The dwarf red buckeye tree is not just a pretty face in the forest; it serves multiple roles, predominantly in woodland ecosystems. This tree might be lesser-known, yet those who delve deeper find it offers a wealth of intriguing attributes. Not only does it contribute to local biodiversity, but it stands as a resilient specimen thriving in assorted conditions. The subsequent sections will explore its ecological significance, sustainable practices for its cultivation, and woodland stewardship techniques that facilitate its preservation.
Exploring the intricacies of the dwarf red buckeye tree reveals its unique characteristics and adaptability, as well as its contributions to the surrounding ecosystem. One might say this tree is somewhat of a underdog in the botanical world, often overshadowed by taller, more ostentatious species, yet it holds its own in myriad ways.
Understanding Woodland Ecosystems
Importance of Biodiversity in Forests
Biodiversity forms the backbone of healthy forests. It enhances resilience against diseases, pests, and climate challenges. A myriad of species, from towering oaks to small shrubs, work together to create an intricate web of life. The dwarf red buckeye tree plays its part in this complex interplay. Its flowers offer food for pollinators, while its leaves provide shelter for various critters.
The presence of diverse species can also foster stability within woodland ecosystems. If one species suffers, others can fill the gap, maintaining ecological balance. When the dwarf red buckeye thrives, it can aid in this balance, serving as a food source for deer and contributing to soil health when its leaves decompose.
Role of Forests in Climate Regulation
Forests are more than just a collection of trees; they are significant players in regulating our climate. They absorb carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate climate change effects. The dwarf red buckeye tree contributes to this function, albeit on a smaller scale than larger trees. Still, its role shouldn't be discounted.
The shade from trees can cool local temperatures, providing a modicum of relief during hot summer days. If you're wandering through a forest with dwarf red buckeyes, you might just notice how much cooler it feels beneath their canopy. More so, they help in managing water cycles, retaining moisture in the soil, which can reduce the risk of drought in nearby areas.
"A healthy ecosystem is like a well-tuned orchestra, with each species playing its part to produce harmony."
Sustainable Forestry Practices
Principles of Sustainable Forestry
Sustainable forestry seeks to balance ecological health with economic viability. The focus isn't simply to cut trees but to manage them in a way that ensures future generations can also benefit. Practices such as selective logging, where only certain trees are harvested, protect the integrity of the ecosystem.
Incorporating the dwarf red buckeye into sustainable forestry practices can enhance both biodiversity and aesthetics. By maintaining its presence alongside more commercially viable tree species, forest managers can create diverse habitats that keep wildlife thriving and landscapes attractive.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Numerous examples exist that highlight sustainable forestry practices in action. For instance, in the Great Smoky Mountains, mixed-species forests, which include trees like the dwarf red buckeye, have seen significant ecological benefits. By fostering diverse habitats, these areas attract a wider variety of wildlife, strengthen the soil, and improve water quality.
Woodland Stewardship Techniques
Forest Management Plans
Developing comprehensive forest management plans is critical for maintaining healthy woodland ecosystems. These plans outline the goals and methods for managing resources effectively, incorporating strategies that include habitat conservation, tree planting, and even community engagement.
For the dwarf red buckeye, a thoughtful management plan can ensure that its unique attributes are preserved and utilized effectively, providing both ecological benefits and aesthetic value. This approach ensures the tree won't just survive but thrive in its habitat.
Conservation Strategies
Effective conservation strategies focus not only on protecting existing trees but also on fostering new growth. Techniques may include controlled burns to encourage new shoots, clear intervals for wildlife movement, and planting young trees to supplement aging populations.
In essence, engaging actively in the stewardship of the dwarf red buckeye tree can set a precedent for holistic woodland care, benefiting the broader ecosystem.
The health of our forests hinges on a collective effort, incorporating methodologies that embrace ecological intricacies while supporting growth of species like the dwarf red buckeye. As we explore this ecological gem further, its myriad benefits and roles in the ecosystem begin to unfurl like the delicate petals of its flowers.
Prologue to the Dwarf Red Buckeye Tree
The dwarf red buckeye tree is often overlooked in discussions about North American flora, yet it holds unique ecological value and aesthetic appeal. This smaller cousin of the larger buckeye trees boasts not only attractive foliage but also contributes significantly to its surrounding ecosystem. In this section, we will explore the importance of the dwarf red buckeye, shedding light on its characteristics, benefits, and considerations.
Importance in Ecosystem and Culture
The dwarf red buckeye is a native plant, which means it plays a critical role in local biodiversity. Its presence supports various species, from pollinators to birds, providing a hospitable environment for wildlife. In regions where this tree grows, one may notice its ability to stabilize soil and control erosion, acting as a natural guardian for the earth.
Furthermore, the tree's striking springtime flowers attract bees and butterflies, crucial for the pollination of many other plants in the area. The seeds produced by the tree are also significant, serving as a food source for local wildlife, including squirrels and birds.
Benefits for Plant Enthusiasts and Gardeners
For those passionate about gardening or landscaping, the dwarf red buckeye offers diverse benefits. Its relatively compact size makes it an ideal choice for gardens that may not have the space for larger trees. When placed strategically, it can provide shade, enhance privacy, and add an interesting vertical element to garden design.
The tree typically grows between 10 to 20 feet and features distinctive palmate leaves. These characteristics make it a conversation starter among gardening communities. Furthermore, it requires minimal maintenance compared to more demanding ornamental trees, making it appealing for both amateur and seasoned horticulturists.
Considerations in Cultivation
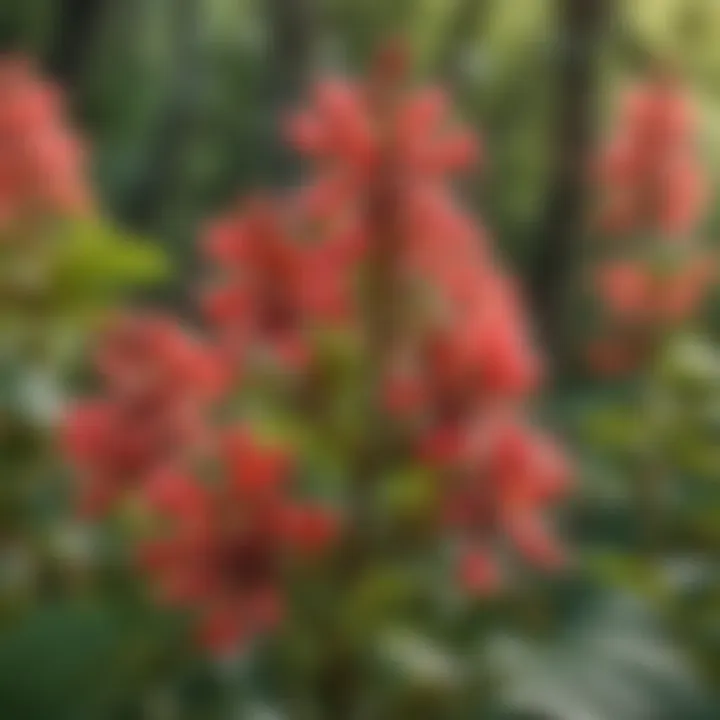

When considering adding the dwarf red buckeye to your planting scheme, it's worth contemplating its site selection and soil preferences. It thrives in well-drained soils and can tolerate a range of pH levels, though it favors slightly acidic conditions. Additionally, while the tree is relatively drought-tolerant once established, it benefits from regular watering, especially during dry spells.
"Understanding the dwarf red buckeye tree's unique properties and ecological role can lead to more sustainable gardening and conservation practices."
The End
In summary, the dwarf red buckeye tree is not only a unique specimen worth exploring for its stunning aesthetic but also a vital component of woodland ecosystems. Its many benefits extend to both the environment and horticultural pursuits, highlighting why it deserves a place in our gardens and conservation efforts. As we delve deeper into the various aspects of this remarkable tree, we will uncover further information about its taxonomy, physical traits, ecological contributions, and practical cultivation techniques.
Taxonomy and Classification
Understanding the taxonomy and classification of the dwarf red buckeye tree is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it offers insights into its evolutionary relationships with other flora, shedding light on its unique traits and adaptations. Secondly, a robust classification aids in the study of its conservation status and ecological roles. By delving into this segment, we can appreciate the intricacies of biodiversity and the interconnectedness within ecosystems, as well as highlight key considerations for professionals engaged in forestry and conservation.
Scientific Name and Family
The dwarf red buckeye tree is scientifically named Aesculus pavia, a member of the Sapindaceae family. This family encompasses a variety of flowering plants, known for their characteristic fruits that often contain a single seed, or a few seeds, encased in a spiky shell.
The name Aesculus derives from an ancient term for oak and suggests a link between the buckeye and this prestigious tree group. The pavia part is a nod to the tree’s native grounds in North America, particularly the southeastern U.S. This connection to its family not only aids in identification but also informs cultivation practices, as understanding related species can help in managing pests and diseases effectively.
Geographical Distribution
The dwarf red buckeye tree is predominantly found in the eastern parts of the United States, favoring habitats ranging from rich woods to moist areas along rivers. In states like Florida, Georgia, Alabama, and into parts of Virginia, this tree thrives beautifully. Its geographical distribution reflects its adaptability, while also hinting at specific environmental preferences that influence its growth.
Interestingly, this tree is often spotted in understory layers of deciduous forests, meaning it's well-suited for shaded environments where it can grow while receiving filtered sunlight. As one traverses through these regions, the vibrant clusters of its reddish flowers provide a stunning pop against a lush green backdrop, marking its presence in these ecosystems.
"The distribution of the dwarf red buckeye tree underscores its adaptability within diverse ecosystems, contributing significantly to localized biodiversity."
The regions where it flourishes also underline the importance of ongoing habitat preservation, as the dwarf red buckeye tree plays a vital role in its ecosystem, serving as food and shelter for various wildlife. Given that its range overlaps with many urban areas, understanding its distribution is crucial for preservation efforts and urban planning as well. By paying attention to the taxonomy and geographical presence of the dwarf red buckeye, forestry practitioners and conservationists can bolster their efforts to maintain harmony in local ecosystems.
Physical Characteristics
Understanding the physical characteristics of the dwarf red buckeye tree is fundamental for anyone looking to integrate this intriguing species into their landscape or research. These characteristics not only define its presence but also influence its role within its ecosystem. The tree's small stature, distinct foliage, and unique flowers all contribute to its overall appeal and ecological function.
Growth Habit and Size
The dwarf red buckeye tree, scientifically known as Aesculus pavia, typically reaches a height of about 10 to 20 feet, which makes it an excellent choice for smaller yards or gardens where larger trees may overwhelm the space. Its growth habit is often characterized by a rounded or bushy form, creating a dense canopy that provides shelter for various species.
The compact height of the dwarf red buckeye permits it to be effectively utilized in landscaping where space is limited, promoting biodiversity without encroaching significantly on surrounding areas.
Usually, the tree grows at a moderate pace and can be easily pruned to maintain an ideal shape. It’s especially noteworthy that, despite its gradual growth, the dwarf red buckeye can live for decades, becoming a long-term investment for ecological landscaping or personal enjoyment.
Leaf Structure and Coloration
The leaves of the dwarf red buckeye are quite distinctive, typically exhibiting a palmate arrangement with five to seven leaflets. Each leaflet is oval-shaped, and they can reach lengths of 3 to 6 inches. In spring, new leaves emerge in a brilliant, fresh green that matures to a darker green over the summer. This seasonal transition adds an extra layer of visual interest as they turn to varying shades of yellow, orange, and red in the fall.
The leaf structure is not only aesthetic but also functional; it plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, enabling the tree to thrive in its environment. Moreover, the glossy coating of the leaves helps resist pests and diseases, making it a hardy choice for gardeners concerned about plant health.
Flowering and Fruit Production
One of the most captivating features of the dwarf red buckeye tree is its striking flowers. In spring, the tree bursts into bloom with clusters of tubular flowers that can be bright red or yellow, often attracting a variety of pollinators, including bees and hummingbirds. These flowers usually bloom from late April to early June, providing a valuable resource at a time when food can be scarce for local wildlife.
Following the flowering period, the tree produces spiky seed capsules that house glossy seeds. The fruit, while interesting in its appearance, is toxic to humans and pets. However, this won't deter wildlife; certain species, like squirrels and birds, are known to consume them. The life cycle of the dwarf red buckeye tree, from its colorful blossoms to its unique fruit, highlights its importance and adaptability in the ecosystem.
In summary, the dwarf red buckeye's physical characteristics—its growth habit, distinctive leaves, and beautiful flowers—are pivotal in understanding its role within both cultivated and wild environments. These traits not only enhance its ornamental value but also signify its ecological importance, making it a worthy subject for further study and appreciation.
Ecological Benefits
The dwarf red buckeye tree plays a pivotal role in its environment, shaping ecosystems while providing numerous ecological benefits. This small but significant tree offers a variety of habitats, supports biodiversity, and contributes to the overall health of the soil. Its various roles can be essential for maintaining ecological balance and promoting sustainability in woodland areas.
Habitat for Local Fauna
One of the notable features of the dwarf red buckeye tree is its capacity to serve as a habitat for numerous species of local fauna. This tree’s dense foliage creates an inviting microhabitat for birds, mammals, and insects. Species such as the eastern tiger swallowtail butterfly and various native birds often seek refuge and food among its branches. The tree's seeds and flowers also provide nourishment for various animals; deer, for example, feast on the leaves.
Moreover, creating a diverse habitat encourages a complex web of interactions among species, which is crucial for a resilient ecosystem. When you think about it, the dwarf red buckeye not only provides shelter but also acts as a stepping stone for wildlife conservation, allowing species populations to thrive.
Pollination Dynamics
Pollination is another fundamental aspect of the dwarf red buckeye tree's ecological role. The vibrant flowers of this tree not only attract a wide array of pollinators, including bees and butterflies, but they also serve as a vital food source early in the spring. Pollinators like the honeybee find the tree’s nectar to be a vital energy source just when food is less plentiful.
While these pollinators work tirelessly, they facilitate the reproduction of the buckeye tree, ensuring its continuation. Through this relationship, the tree supports the ongoing vitality of pollinator populations, which are increasingly threatened in many parts of the world. Thus, the presence of the dwarf red buckeye can be viewed as a significant player in fostering healthy pollination dynamics in its environment.
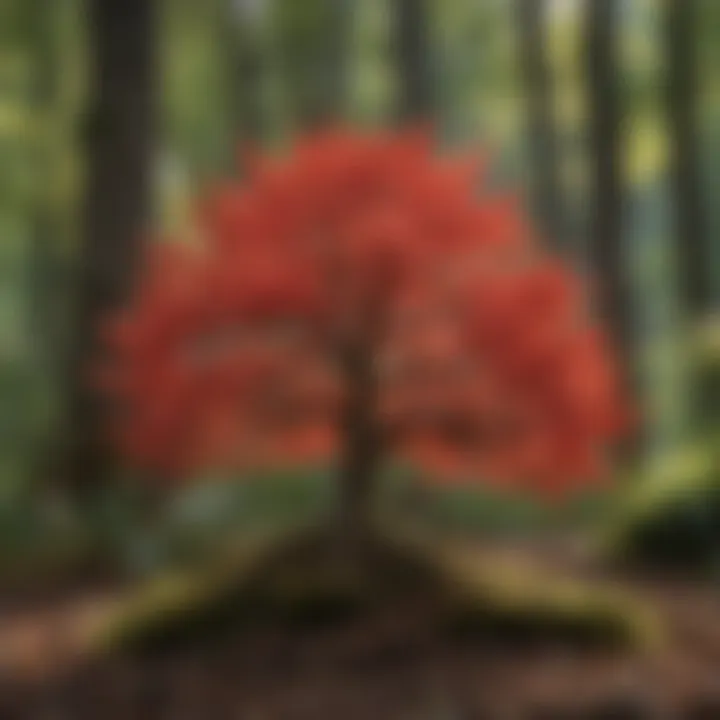


Soil Health and Stabilization
The dwarf red buckeye tree also plays a crucial role in maintaining soil health and stabilization. Its root system helps bind the soil together, preventing erosion and promoting stability in its surroundings. This process is particularly important in areas prone to heavy rainfall or on slopes where soil can easily wash away.
In addition to preventing erosion, the tree contributes organic matter to the soil when leaves fall and decompose. As these leaves break down, they add nutrients back into the earth, enriching the ecosystem surrounding it. This nutrient cycling is beneficial for both the dwarf red buckeye and adjacent flora, allowing for a thriving forest community.
Overall, the dwarf red buckeye tree supports numerous ecological functions that extend beyond its immediate presence. From providing habitat to fostering pollination and enhancing soil health, every aspect of this tree contributes to the broader ecosystem's vitality and resilience. As we explore its significance, it's clear that this tree is not merely a decorative feature but a critical component of environmental health.
"In preserving native flora like the dwarf red buckeye, we are investing in the future of our ecosystems."
Integrating these benefits into our conservation efforts, as well as understanding these dynamics, is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and ecological integrity.
Cultivation Practices
Cultivating the dwarf red buckeye tree offers many benefits, not only enriching your garden but also contributing positively to the local ecosystem. This tree, known for its beauty and ecological significance, requires specific care practices to thrive. Understanding how to cultivate it isn’t just about planting; it involves knowing the right site conditions, watering, nutrition, and maintenance techniques. This ensures not only a flourishing tree but a sustainable addition to your environment.
Site Selection and Soil Requirements
When choosing a site for your dwarf red buckeye tree, it's crucial to consider several factors. This tree flourishes best in well-drained soils that are rich in organic matter. The ideal soil pH level generally ranges from 5.5 to 7.0. Loamy to sandy soils often work wonders. It's common to underestimate drainage; poor soil that retains water can lead to root rot, which is a real killer.
Key considerations for site selection include:
- Sunlight: Aim for a location that provides partial shade to full sun, as these trees can be sensitive to extreme heat.
- Space: Give them enough room to grow—dwarf red buckeyes can still reach widths of up to 15 feet.
- Local Climate: They do best in USDA zones 4 through 9.
A soil test can often guide amendments that might be necessary to create a thriving environment for these trees. If you're struggling with heavy clay soil, adding compost can help improve its structure and drainage.
Watering and Nutritional Needs
Proper hydration is a cornerstone of healthy growth. When the dwarf red buckeye is first planted, consistent watering is important. Typically, you want to water deeply once a week during dry spells, giving the roots a chance to reach far down. Once established, the tree is somewhat drought-tolerant, but don't let it go completely dry; those leaves will droop, making it quite unhappy.
In terms of nutrition, consider a balanced fertilizer in early spring to boost growth. Organic options, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can promote soil health and maintain nutrient levels. Observe your tree for any signs of nutrient deficiency such as yellowing leaves, as these can be indicators that adjustments are needed.
Pruning and Maintenance Techniques
Maintaining the dwarf red buckeye is straightforward with a little knowledge. Pruning is best done in late winter or early spring before new growth begins. This not only helps shape the tree but also removes any dead or diseased wood. A clean cut with sharp tools promotes quicker healing and less chance for infection.
Maintenance tips to consider:
- Shape the canopy: Aim for a well-balanced look, allowing light to penetrate through the branches.
- Inspect regularly: Check for pests and diseases that can sabotage your efforts. Act early when you notice any signs of trouble.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of mulch can suppress weeds, retain moisture, and regulate soil temperature.
Keeping these practices on hand would certainly foster a healthy environment for your dwarf red buckeye tree. Regular attention will yield not just a beautiful specimen but a living contribution to the local biodiversity.
Pest and Disease Management
Understanding pest and disease management is vital for the health and longevity of the dwarf red buckeye tree. For those nurturing these trees, knowledge about potential threats can mean the difference between a thriving specimen and a moribund one. This segment will discuss common pests, effective prevention strategies, and the importance of ongoing management practices. Addressing these concerns not only preserves the beauty and vitality of the dwarf red buckeye but also contributes to the ecological stability of the surrounding environment.
Common Pests Affecting Dwarf Red Buckeye
The dwarf red buckeye can fall prey to various pests, each presenting distinct challenges. Here are some significant offenders that might lead to complications in plant health:
- Aphids: These small, sap-sucking insects often congregate on new growth, leading to distorted leaves and potential transmission of viruses.
- Spider Mites: Particularly in dry conditions, spider mites can rapidly proliferate, creating a fine webbing on leaves and reducing their overall vigor.
- Scale Insects: These pests tend to camouflage themselves on stems and leaves, making them hard to spot. Their feeding can weaken the tree, resulting in premature leaf drop.
- Borers: Wood-boring insects can hollow out the tissues by tunneling, which may cause structural damage over time.
It's crucial for gardeners and land managers to frequently inspect the trees. An early detection means a proactive approach in dealing with these pests, often leading to a more successful management strategy.
Disease Prevention Strategies
Preventing diseases is equally as essential as managing pests. The dwarf red buckeye can experience several common diseases that, while not always fatal, can detract significantly from its health. Here are several strategies to ensure the tree stays disease-free:
- Proper Spacing and Air Circulation: Planting trees with adequate spacing allows for better air movement around the leaves, reducing humidity and preventing fungi from establishing themselves.
- Cultural Practices: Regular mulching around the base can trap moisture, but be careful to not over-water as this can lead to root rot.
- Chemical Controls: In severe cases, the use of insecticidal soaps or fungicides may be necessary. Always choose targeted applications to reduce harmful effects on beneficial insects and the surrounding ecosystem.
- Observation and Rapid Response: Keep an eye out for signs of distress, such as wilting or leaf discolouration. A keen eye can lead to timely interventions, potentially saving the tree from further decline.
"A proactive approach, understanding the interplay of pests and diseases, is the cornerstone of effective management for the dwarf red buckeye tree."
Ornamental Uses
The dwarf red buckeye tree is not just a plant that enriches ecosystems but also serves as a notable ornamental feature in many landscapes. Incorporating this unique tree into gardens or public spaces presents various design and aesthetic advantages that can transform the atmosphere of an area. Its characteristic elegance and vibrant clusters of flowers make it a favored choice among landscape architects and homeowners alike.
Landscaping and Design Considerations
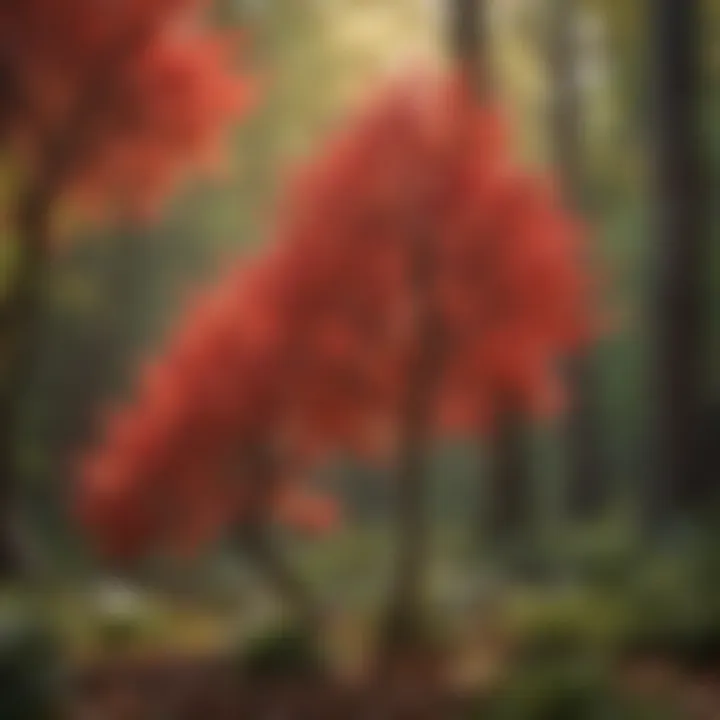


When thinking about the dwarf red buckeye in terms of landscape design, there are several factors to take into account. This tree thrives in dappled sunlight and does well in rich, well-drained soils. Strategically planting it in a location that receives partial shade can maximize both its growth and visual appeal.
One element to consider is its size and shape. Generally, this tree matures to a manageable height, making it perfect for small to medium-sized gardens. Its rounded crown creates an inviting, lush space without overwhelming surrounding plants. Additionally, mixing it with complementary trees such as red maples or sweetgums can create a visually striking scene. Grouping it amidst other flowering plants, such as hostas or ferns, will provide a rich tapestry of color and texture throughout the seasons.
- Color Palette: The bright flowers of the dwarf red buckeye in spring can contrast beautifully with the deep greens of surrounding foliage. Their fire-red blossoms can act as focal points in garden beds.
- Seasonal Interest: This tree does not merely look appealing in one season. In the fall, its leaves can exhibit a mesmerizing mix of yellow and orange, which attract attention and beautify landscapes.
- Ecological Design: Considering the ecological benefits of this tree, such as attracting pollinators, enhances its role in landscaping. Planting them alongside perennials can promote biodiversity.
Seasonal Aesthetic Appeal
The seasonal transformation of the dwarf red buckeye adds yet another layer to its ornamental value.
- Spring Blooming: Come spring, the profusion of tubular flowers will paint the landscape in brilliant red, drawing hummingbirds and butterflies. This creates a lively, engaging atmosphere that encourages interaction with nature.
- Summer Foliage: In summer, the tree’s glossy leaves provide a lush canopy that offers respite from the sun. Its dense foliage can serve as a natural screen, enhancing privacy without obstructing airflow.
- Autumn Spectacle: When fall rolls around, the leaves shift hues, offering a stunning display of color that marks the change of seasons. The combination of the tree's shape and vibrant foliage can make any garden feel warm and inviting.
- Winter Framework: During winter, while the tree may seem bare, its unique form can still provide structure and create a picturesque scene against snow. The contrasting skeletal branches can lend an artistic touch to winter landscapes.
"In landscape design, the dwarf red buckeye stands out not just for its visual appeal but for its contribution to supporting wildlife and thrumming ecosystems."
These ornamental uses of the dwarf red buckeye tree underscore its multifaceted role in aesthetics and ecology. With these considerations, one can appreciate how the dwarf red buckeye tree, with its seasonal changes, offers an enriching experience both for human observers and the wildlife that share its habitat.
Cultural Significance
The dwarf red buckeye tree isn't just a pretty face in the landscape; it carries profound cultural significance woven through history, tradition, and symbolism. As one delves into its role, insights emerge about interconnections between local communities and this striking species. Such explorations reveal how cultures adapt and thrive, and how nature's offerings manifest in various aspects of life.
Historical Context and Use in Traditional Practices
Looking back, the dwarf red buckeye has been more than just an ornamental fixture. Indigenous peoples recognized its value long before modern gardening took off. The seeds, which are known for their shiny, reddish-brown exterior, were traditionally used as natural beads. They became a part of jewelry, ceremonial attire, and even indigenous games, showcasing an interplay of functionality and aesthetics that defines indigenous craftsmanship.
Moreover, traditional medicine practices sometimes incorporated parts of the tree. While the seeds are toxic if ingested, various recipes emerged that utilized other elements like leaves for potential medicinal applications. This highlights a greater understanding of nature's resources, pointing to a relationship brimming with respect and knowledge handed down through generations.
Symbolism in Art and Literature
In art and literature, the dwarf red buckeye finds its way into numerous discussions and depictions. Its striking flowers, with vibrant red and yellow hues, symbolize passion, observation, and grounding. Various works have drawn inspiration from nature, and the buckeye tree often represents endurance within a broader motif of western forests.
The tree's life cycle speaks volumes, from blooming in early spring to shedding its leaves in autumn. In literature, it becomes a metaphor for transformation and change, resonating with themes of resilience and continuity. The imagery of these graceful trees populates poetry, painting, and storytelling, allowing cultures to express emotional landscapes that often mirror the natural world around them.
"Nature always wears the colors of the spirit." — Ralph Waldo Emerson
In summary, the dwarf red buckeye tree transcends its ordinary existence. Its contributions to cultural practices, along with its enduring symbolism in art and literature, weave a rich tapestry of significance deserving exploration. The seed of knowledge sown by this tree expands our understanding—of history, identity, and the intricate ties binding man and nature.
Conservation Concerns
The conservation of the dwarf red buckeye tree is an important aspect of fostering biodiversity and maintaining the health of woodland ecosystems. The unique characteristics of this species not only offer aesthetic value but also serve several ecological functions. As environmental awareness grows, understanding the conservation concerns surrounding the dwarf red buckeye and its native populations will equip forestry professionals and conservation enthusiasts with the knowledge needed to protect this remarkable tree.
Threats to Native Populations
The dwarf red buckeye tree faces various threats, which can impact both individual trees and overall populations. Some of the most pressing challenges include habitat loss, climate change, and invasive species.
- Habitat Loss: Urban development, deforestation, and agricultural expansion can lead to significant loss of habitat for the dwarf red buckeye. As human activities increase, natural habitats are compromised, making it difficult for these trees to thrive.
- Climate Change: Shifting climate patterns affect the growth and reproduction of many tree species, including the dwarf red buckeye. Variations in temperature and precipitation can disrupt seasonal cycles that are critical for the tree’s lifecycle.
- Invasive Species: Non-native plants and pests can outcompete or directly harm the dwarf red buckeye. Invasive species often exploit the weakened ecosystems caused by habitat loss and climate fluctuations.
Managing these threats requires a concerted effort from conservationists, local communities, and forestry professionals. Without adequate attention and intervention, the populations of dwarf red buckeyes may decline, leading to a loss of genetic diversity and ecological function.
Conservation Efforts and Community Involvement
Many organizations and communities are actively working to conserve the dwarf red buckeye and its habitat. These efforts play a vital role in ensuring the survival of this tree species and the ecosystems to which it belongs.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness in local communities about the importance of the dwarf red buckeye helps foster a sense of responsibility. Educational programs in schools and community workshops can enhance understanding of the species and its ecological significance.
- Restoration Projects: Engaging local volunteers in reforestation and habitat restoration initiatives is crucial. Planting dwarf red buckeyes alongside other native species can help restore natural balance in local ecosystems.
- Collaboration with Local Governments: Conservation groups can work with governments to develop policies that protect the habitats of the dwarf red buckeye. This could include establishing protected areas or enforcing regulations against deforestation.
"The health of our forests and the survival of species like the dwarf red buckeye depend on our collective action. Conservation is not just a task; it is a commitment to future generations."
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing research is vital to understanding the specific needs and threats to dwarf red buckeye trees. Monitoring programs can track population health and inform conservation strategies.
Through these combined efforts, communities can contribute to the preservation of the dwarf red buckeye, ensuring that this remarkable tree continues to enrich our landscapes and ecosystems for years to come.
Epilogue
In summarizing the exploration of the dwarf red buckeye tree, it’s essential to underscore its multifaceted significance within the tapestry of our ecosystems and the intriguing interplay it has with human culture. This tree isn't just another leafy companion in our woods; it carries with it a wealth of ecological and ornamental benefits that enhance both our environment and our aesthetic experiences.
Firstly, the dwarf red buckeye serves as a vital player in maintaining local biodiversity. It offers habitat for various wildlife species, from birds to insects, aiding in the continuity of local ecosystems. Its flowers attract pollinators, which are critical in sustaining many other plant species, not just the buckeye itself. The tree’s ability to contribute to soil health also cannot be overlooked—it fortifies the ground, making it more resilient against erosion and promoting a healthy habitat for undergrowth flora.
Moreover, this guide highlights essential cultivation techniques that anyone looking to incorporate this tree into their landscape should consider. A good understanding of its water and nutritional requirements, as well as seasonal maintenance, sets the stage for a thriving plant. Engaging in these practices not only ensures a beautiful addition to one’s property but also fosters a sense of stewardship toward the environment.
In practical terms, the dwarf red buckeye tree presents unique opportunities for design in landscaping. Its aesthetic qualities, particularly during blooming seasons, contribute to visually striking gardens and parks, enriching the communal spaces we cherish. The cultural narratives surrounding the tree further enhance its importance, as it symbolizes resilience and growth, resonating deeply with various communities.
With the ongoing threats to its native populations due to climate change and habitat destruction, efforts toward conservation take on critical importance. This discussion has emphasized the role of community involvement in restoring and preserving natural habitats where the dwarf red buckeye can flourish.
"Conservation is not merely a practice; it is a testament to how we value our natural heritage and the future we envision."
Ultimately, this exploration of the dwarf red buckeye tree serves as a reminder of the intricate relationships we have with natural elements. By understanding and appreciating its role, we can better engage with our environment, ensuring that we pass on a legacy of biodiversity and beauty to future generations.







